A role for proprioceptors in sngception
- PMID: 39888990
- PMCID: PMC11784836
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abc5219
A role for proprioceptors in sngception
Abstract
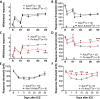
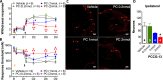
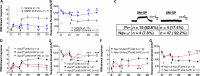
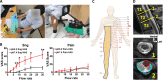
Proprioceptors are primary mechanosensory neurons to monitor the status of muscle contraction and/or body position (1). Although proprioceptors are known as non-nociceptive mechanoreceptors, they also express the pro-nociceptive acid-sensing ion channel 3 (ASIC3) (2-5). To probe the role for proprioceptors in sensing acidosis (or sngception) (6), we found that genetic deletion of Asic3 in proprioceptors but not in nociceptors abolished acid-induced chronic hyperalgesia in mice. Chemo-optogenetically activating proprioceptors resulted in hyperalgesic priming that favored chronic pain induced by acidosis. In humans, intramuscular acidification induced acid perception but not pain. Conversely, in a spinal cord-injured patient who lost pain sensation in the right leg, proprioception and sngception were remaining somatosensory functions, associated with the spinal dorsal column. Together, evidence from both mouse and human studies suggests a role for proprioceptors in sngception.
Figures

References
-
- Kröger S., Proprioception 2.0: Novel functions for muscle spindles. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 31, 592–598 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Deval E., Lingueglia E., Acid-sensing ion channels and nociception in the peripheral and central nervous systems. Neuropharmacology 94, 49–57 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Sluka K. A., Price M. P., Breese N. M., Stucky C. L., Wemmie J. A., Welsh M. J., Chronic hyperalgesia induced by repeated acid injections in muscle is abolished by the loss of ASIC3, but not ASIC1. Pain 106, 229–239 (2003). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

