Touch-evoked traveling waves establish a translaminar spacetime code
- PMID: 39889002
- PMCID: PMC11784861
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adr4038
Touch-evoked traveling waves establish a translaminar spacetime code
Abstract
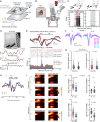
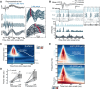
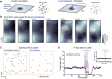
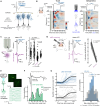
Linking sensory-evoked traveling waves to underlying circuit patterns is critical to understanding the neural basis of sensory perception. To form this link, we performed simultaneous electrophysiology and two-photon calcium imaging through transparent NeuroGrids and mapped touch-evoked traveling waves and underlying microcircuit dynamics. In awake mice, both passive and active whisker touch elicited traveling waves within and across barrels, with a fast early component followed by a late wave that lasted hundreds of milliseconds poststimulus. Notably, late waves were modulated by perceived value and predicted behavioral choice in a two-whisker discrimination task. We found that the late wave feature was (i) modulated by motor feedback, (ii) differentially engaged a sparse ensemble reactivation pattern across layer 2/3, which a balanced-state network model reconciled via feedback-induced inhibitory stabilization, and (iii) aligned to regenerative layer 5 apical dendritic Ca2+ events. Our results reveal that translaminar spacetime patterns organized by cortical feedback support sparse touch-evoked traveling waves.
Figures



Update of
-
A Translaminar Spacetime Code Supports Touch-Evoked Traveling Waves.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 9:2024.05.09.593381. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.09.593381. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Adv. 2025 Jan 31;11(5):eadr4038. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adr4038. PMID: 38766232 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

