STICI: Split-Transformer with integrated convolutions for genotype imputation
- PMID: 39890780
- PMCID: PMC11785734
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56273-3
STICI: Split-Transformer with integrated convolutions for genotype imputation
Abstract
Despite advances in sequencing technologies, genome-scale datasets often contain missing bases and genomic segments, hindering downstream analyses. Genotype imputation addresses this issue and has been a cornerstone pre-processing step in genetic and genomic studies. Although various methods have been widely adopted for genotype imputation, it remains challenging to impute certain genomic regions and large structural variants. Here, we present a transformer-based framework, named STICI, for accurate genotype imputation. STICI models automatically learn genome-wide patterns of linkage disequilibrium, evidenced by much higher imputation accuracy in regions with highly linked variants. Our imputation results on the human 1000 Genomes Project and non-human genomes show that STICI can achieve high imputation accuracy comparable to the state-of-the-art genotype imputation methods, with the additional capability to impute multi-allelic variants and various types of genetic variants. STICI can be trained for any collection of genomes automatically using self-supervision. Moreover, STICI shows excellent performance without needing any special presuppositions about the underlying patterns in collections of non-human genomes, pointing to adaptability and applications of STICI to impute missing genotypes in any species.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
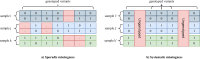
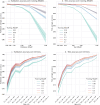

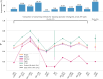
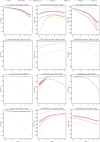
Similar articles
-
A comprehensive evaluation of SNP genotype imputation.Hum Genet. 2009 Mar;125(2):163-71. doi: 10.1007/s00439-008-0606-5. Epub 2008 Dec 17. Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19089453
-
Evaluating Imputation Algorithms for Low-Depth Genotyping-By-Sequencing (GBS) Data.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 18;11(8):e0160733. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160733. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27537694 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype imputation methods for whole and complex genomic regions utilizing deep learning technology.J Hum Genet. 2024 Oct;69(10):481-486. doi: 10.1038/s10038-023-01213-6. Epub 2024 Jan 15. J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38225263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molgenis-impute: imputation pipeline in a box.BMC Res Notes. 2015 Aug 19;8:359. doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1309-3. BMC Res Notes. 2015. PMID: 26286716 Free PMC article.
-
Two-stage strategy using denoising autoencoders for robust reference-free genotype imputation with missing input genotypes.J Hum Genet. 2024 Oct;69(10):511-518. doi: 10.1038/s10038-024-01261-6. Epub 2024 Jun 25. J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38918526 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GENA-LM: a family of open-source foundational DNA language models for long sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 11;53(2):gkae1310. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1310. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39817513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torkamaneh, D., Belzile, F. Accurate imputation of untyped variants from deep sequencing data. Methods Mol. Biol. 271–281 10.1007/978-1-0716-1103-6_13 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Das, S., Abecasis, G. R. & Browning, B. L. Genotype imputation from large reference panels. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet.19, 73–96 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

