Oral submucous fibrosis: pathogenesis and therapeutic approaches
- PMID: 39890798
- PMCID: PMC11785813
- DOI: 10.1038/s41368-024-00344-6
Oral submucous fibrosis: pathogenesis and therapeutic approaches
Abstract
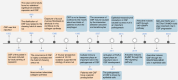
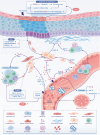
Oral submucous fibrosis (OSF), characterized by excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) that causes oral mucosal tissue sclerosis, and even cancer transformation, is a chronic, progressive fibrosis disease. However, despite some advancements in recent years, no targeted antifibrotic strategies for OSF have been approved; likely because the complicated mechanisms that initiate and drive fibrosis remain to be determined. In this review, we briefly introduce the epidemiology and etiology of OSF. Then, we highlight how cell-intrinsic changes in significant structural cells can drive fibrotic response by regulating biological behaviors, secretion function, and activation of ECM-producing myofibroblasts. In addition, we also discuss the role of innate and adaptive immune cells and how they contribute to the pathogenesis of OSF. Finally, we summarize strategies to interrupt key mechanisms that cause OSF, including modulation of the ECM, inhibition of inflammation, improvement of vascular disturbance. This review will provide potential routes for developing novel anti-OSF therapeutics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Warnakulasuriya, S. et al. Oral potentially malignant disorders: a consensus report from an international seminar on nomenclature and classification, convened by the WHO Collaborating Centre for Oral Cancer. Oral. Dis.27, 1862–1880 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Sirsat, S. M. et al. Submucous fibrosis of the palate in diet-preconditioned Wistar rats. Induction by local painting of capsaicin-an optical and electron microscopic study. Arch. Pathol.70, 171–179 (1960). - PubMed
-
- Pindborg, J. J. et al. Frequency of oral carcinoma, leukoplakia, leukokeratosis, leukoedema, submucous fibrosis, and lichen planus in 10,000 Indians in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India; preliminary report. J. Dent. Res.44, 61 (1965). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

