Genome-wide gene expression profiles throughout human malaria parasite liver stage development in humanized mice
- PMID: 39891010
- PMCID: PMC11790487
- DOI: 10.1038/s41564-024-01905-5
Genome-wide gene expression profiles throughout human malaria parasite liver stage development in humanized mice
Abstract
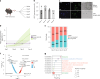
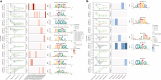
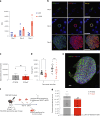
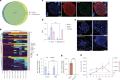
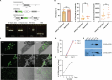
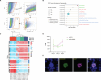
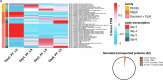
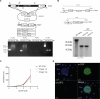
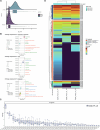
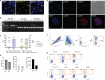
Gene expression of Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) liver-stage (LS) parasites has remained poorly characterized, although they are major vaccine and drug targets. Using a human liver-chimaeric mouse model and a fluorescent parasite line (PfNF54CSPGFP), we isolated PfLS and performed transcriptomics on key LS developmental phases. We linked clustered gene expression to ApiAP2, a major family of transcription factors that regulate the parasite life cycle. This provided insights into transcriptional regulation of LS infection and expression of essential LS metabolic and biosynthetic pathways. We observed expression of antigenically variant PfEMP1 proteins and the major Pf protein export machine PTEX and identified protein candidates that might be exported by LS parasites. Comparing Pf and P. vivax LS transcriptomes, we uncovered differences in their expression of sexual commitment factors. This data will aid LS research and vaccine and drug target identification for prevention of malaria infection.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: E.L.F., V.C. and M.E.F. are employees of Novartis Pharma AG. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- World Malaria Report 2022. (World Health Organization, 2022); https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240064898
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

