CircRNF13 enhances IGF2BP1 phase separation-mediated ITGB1 mRNA stabilization in an m6A-dependent manner to promote oral cancer cisplatin chemoresistance
- PMID: 39891203
- PMCID: PMC11783750
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-025-02239-4
CircRNF13 enhances IGF2BP1 phase separation-mediated ITGB1 mRNA stabilization in an m6A-dependent manner to promote oral cancer cisplatin chemoresistance
Abstract
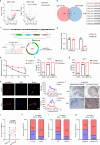
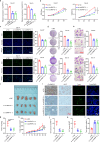
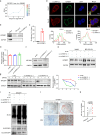
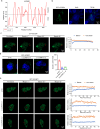
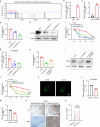
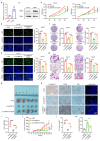
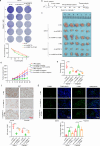
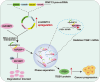
Oral cancer ranks among the most common malignancies within the head and neck region; however, its etiology remains inadequately understood despite substantial research advances in recent years. Many studies highlight the regulatory role of circular RNAs (circRNAs) in human cancers, suggesting their potential as cancer biomarkers. However, their specific mechanisms in oral cancer are not well understood. This study analyzed circRNAs expression in oral cancer, identifying circRNF13 (circbaseID: has_circ_0006801) as having elevated expression in oral cancer cells and tissues. Our study demonstrated that circRNF13 is correlated with increased tumor grade and stage in oral cancer. Results from both in vitro and in vivo experiments indicated that circRNF13 enhances cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth, while concurrently diminishing tumor sensitivity to cisplatin. Mechanistically, circRNF13 interacts with the m6A "reader" protein IGF2BP1, inhibiting its ubiquitin-mediated degradation and promoting its phase separation formation. Subsequently, circRNF13 augments the stability of ITGB1 mRNA via IGF2BP1 in a manner dependent on m6A modification. The m6A modification of ITGB1 mRNA is modulated by the phase separation of IGF2BP1, thereby promoting the malignant progression of oral cancer cells. This evidence positions circRNF13 as a crucial regulatory molecule in the pathogenesis of oral cancer and suggests its potential as a therapeutic target. This discovery enriches our understanding of the mechanistic role of circRNAs.
Keywords: IGF2BP1; Liquid-liquid phase separation; Oral cancer; circRNF13; m6A.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hunan Cancer Hospital. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- de Morais EF, Almangush A, Salo T, da Silva SD, Kujan O, Coletta RD. Emerging histopathological parameters in the prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinomas. Histol Histopathol. 2024;39(1):1–12. - PubMed
-
- Zhang XO, Wang HB, Zhang Y, Lu X, Chen LL, Yang L. Complementary sequence-mediated exon circularization. Cell. 2014;159(1):134–47. - PubMed
-
- Kristensen LS, Jakobsen T, Hager H, Kjems J. The emerging roles of circRNAs in cancer and oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022;19(3):188–206. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

