Effective in vivo binding energy landscape illustrates kinetic stability of RBPJ-DNA binding
- PMID: 39893191
- PMCID: PMC11787368
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56515-4
Effective in vivo binding energy landscape illustrates kinetic stability of RBPJ-DNA binding
Abstract
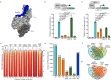
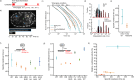
Transcription factors (TFs) such as RBPJ in Notch signaling bind to specific DNA sequences to regulate transcription. How TF-DNA binding kinetics and cofactor interactions modulate gene regulation is mostly unknown. We determine the binding kinetics, transcriptional activity, and genome-wide chromatin occupation of RBPJ and mutant variants by live-cell single-molecule tracking, reporter assays, and ChIP-Seq. Importantly, the search time of RBPJ exceeds its residence time, indicating kinetic rather than thermodynamic binding stability. Impaired RBPJ-DNA binding as in Adams-Oliver-Syndrome affect both target site association and dissociation, while impaired cofactor binding mainly alters association and unspecific binding. Moreover, our data point to the possibility that cofactor binding contributes to target site specificity. Findings for other TFs comparable to RBPJ indicate that kinetic rather than thermodynamic DNA binding stability might prevail in vivo. We propose an effective in vivo binding energy landscape of TF-DNA interactions as instructive visualization of binding kinetics and mutation-induced changes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 427512076/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 468578170/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 422780363/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 316249678/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 450627322/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 447235146/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- TRR81- A12/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 217328187)/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 637987/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 1715822/National Science Foundation (NSF)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

