On QSPR analysis of pulmonary cancer drugs using python-driven topological modeling
- PMID: 39893301
- PMCID: PMC11787360
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-88419-0
On QSPR analysis of pulmonary cancer drugs using python-driven topological modeling
Abstract
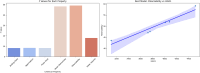
In this paper, we discussed the role of topological descriptors in the QSPR modeling of pulmonary cancer drugs. Degree-based topological indices were computed using computational methods driven by Python that are mathematical representations of properties of molecules without physical measurement. These descriptors were analyzed through linear regression models using SPSS software to predict significant physicochemical properties like boiling point, flash point, molar refractivity, and polarizability. The results show excellent correlations between the computed indices and the observed properties, except for flash point, which ascertains the dependability of the approach in QSPR analysis. The integration of computational and mathematical chemistry will make it easier to evaluate drugs because it can assure consistent data for preclinical development. The paper also reveals specific indices that are superior to others regarding predictive accuracy, thus giving a basis for refining the models to suit the individual compound. This review sets the pace for establishing methodologies that are efficient in designing new and efficient treatments against cancer since it gives insight into the strengths and limitations of topological modeling. This work marked the transformation in accelerating the math involved in drug discovery to reduce such research costs.
Keywords: Linear regression model; Networks; Pulmonary cancer drugs; Python technique; Topological descriptor.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
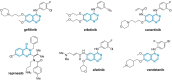





References
-
- Zhou, R. et al. Mechanistic insights into Yifei Sanjie Pill’s regulation of EMT to enhance Gefitinib treatment effect in NSCLC by in silico analysis and experimental validation. J. Ethnopharmacol.4(3), 134–157 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Feng, X., Ma, Z., Yu, C. & Xin, R. MRNDR: multihead attention-based recommendation network for drug repurposing. J. Chem. Inf. Model.64(7), 2654–2669 (2024). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

 confers gefitinib resistance in lung adenocarcinoma through promoting AKR1C1-mediated ferroptosis defense. Cell Death Discov.10(1), 131–145 (2024).
-
confers gefitinib resistance in lung adenocarcinoma through promoting AKR1C1-mediated ferroptosis defense. Cell Death Discov.10(1), 131–145 (2024).
-
