Lessons (to be) learned from liquid biopsies: assessment of circulating cells and cell-free DNA in cancer and pregnancy-acquired microchimerism
- PMID: 39893314
- PMCID: PMC11787191
- DOI: 10.1007/s00281-025-01042-z
Lessons (to be) learned from liquid biopsies: assessment of circulating cells and cell-free DNA in cancer and pregnancy-acquired microchimerism
Abstract
Tumors constantly shed cancer cells that are considered the mediators of metastasis via the blood stream. Analysis of circulating cells and circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) in liquid biopsies, mostly taken from peripheral blood, have emerged as powerful biomarkers in oncology, as they enable the detection of genomic aberrations. Similarly, liquid biopsies taken from pregnant women serve as prenatal screening test for an abnormal number of chromosomes in the fetus, e.g., via the analysis of microchimeric fetal cells and cfDNA circulating in maternal blood. Liquid biopsies are minimally invasive and, consequently, associated with reduced risks for the patients. However, different challenges arise in oncology and pregnancy-acquired liquid biopsies with regard to the analyte concentration and biological (background) noise among other factors. In this review, we highlight the unique biological properties of circulating tumor cells (CTC), summarize the various techniques that have been developed for the enrichment, detection and analysis of CTCs as well as for analysis of genetic and epigenetic aberrations in cfDNA and highlight the range of possible clinical applications. Lastly, the potential, but also the challenges of liquid biopsies in oncology as well as their translational value for the analysis of pregnancy-acquired microchimerism are discussed.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Cell-free DNA; Circulating tumor DNA; Circulating tumor cells; Liquid biopsy; Pregnancy-acquired microchimerism.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
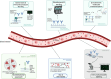
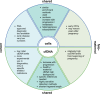
References
-
- Aceto N, Bardia A, Miyamoto DT, Donaldson MC, Wittner BS, Spencer JA, Yu M, Pely A, Engstrom A, Zhu H, Brannigan BW, Kapur R, Stott SL, Shioda T, Ramaswamy S, Ting DT, Lin CP, Toner M, Haber DA, Maheswaran S (2014) Circulating tumor cell clusters are oligoclonal precursors of breast cancer metastasis. Cell 158:1110–1122 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pantel K, Alix-Panabières C (2010) Circulating tumour cells in cancer patients: challenges and perspectives. Trends Mol Med 16:398–406 - PubMed
-
- Pantel K, Alix-Panabieres C (2019) Liquid biopsy and minimal residual disease - latest advances and implications for cure. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 16:409–424 - PubMed
-
- Chang L, Zhu X, Li R, Wu H, Chen W, Chen J, Liu H, Li S, Liu P (2021) A novel method for noninvasive diagnosis of monogenic diseases from circulating fetal cells. Prenat Diagn 41:400–408 - PubMed
-
- Mueller UW, Hawes CS, Wright AE, Petropoulos A, DeBoni E, Firgaira FA, Morley AA, Turner DR, Jones WR (1990) Isolation of fetal trophoblast cells from peripheral blood of pregnant women. Lancet 336:197–200 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

