Redefining outcomes of ventricular arrhythmia for SGLT2 inhibitor medication in heart failure patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 39893467
- PMCID: PMC11786358
- DOI: 10.1186/s13643-025-02766-7
Redefining outcomes of ventricular arrhythmia for SGLT2 inhibitor medication in heart failure patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have been shown to lower the risk of re-hospitalization and cardiovascular mortality among heart failure (HF) patients. Nevertheless, the impact of these agents on ventricular arrhythmias (VAs) has not been thoroughly investigated. To assess the beneficial impact of SGLT2 inhibitors on VAs in patients at various stages of HF, a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials involving SGLT2 inhibitors in this patient population was performed.
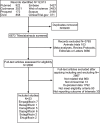
Methods: A comprehensive search of the PubMed, Embase, Ovid, ProQuest, Scopus, and Cochrane databases was performed for clinical trials published up to November 21, 2024. The primary outcomes of interest were incidences of VAs and sudden cardiac death (SCD) between the groups receiving SGLT2 inhibitors and the control drugs. For the outcomes observed in the populations of the included trials and in specific subgroups, hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were pooled and meta-analysed across the analyses.
Results: A total of 23 randomized trials (22 placebo-controlled trials and 1 active-controlled trial) involving 74,380 patients (37,372 receiving SGLT2 inhibitors and 37,008 in the control group) were included. The analysed SGLT2 inhibitors included canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, bexagliflozin, sotagliflozin, and ertugliflozin. The participants were non-advanced HF patients, including at-risk for HF, pre-HF, and symptomatic HF, with follow-up duration ranging from 12 to 296 weeks. Compared with the control, treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors was associated with significantly reduced risk of VAs (risk ratio (RR) 0.85, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.74-0.98; P = 0.02) and SCD (RR 0.79, 95% CI 0.64-0.98; P = 0.03). Subgroup analyses indicated that longer follow-up (≥ 1 year) taking SGLT2 inhibitors can still reduce the risk of VAs (RR 0.79, 95% CI 0.65-0.96; P = 0.02) and SCD (RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.65-0.99; P = 0.04).
Conclusion: SGLT2 inhibitors have beneficial effects on lowering risks of VAs and SCD in patients with type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), and heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF), with longer follow-up duration reinforcing these findings. However, future prospective trials are needed to verify the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on VAs and SCD.
Systematic review registration: PROSPERO (CRD42024601914).
Keywords: Heart failure; Meta-analysis; SGLT2 inhibitor; Sudden cardiac death; Ventricular arrhythmias.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All the authors provided consent for publication. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022;145(18):e895–1032. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

