Spatial and temporal predictability drive foraging movements of coastal birds
- PMID: 39893488
- PMCID: PMC11787743
- DOI: 10.1186/s40462-025-00531-y
Spatial and temporal predictability drive foraging movements of coastal birds
Abstract
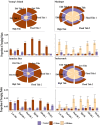
Background: Temporal and spatial predictability of food resources are critical to the foraging efficiency of central place foragers. While site fidelity is often assessed in this context, route fidelity, or the repeated use of the same path while traveling, and temporal aspects of habitat predictability have received less attention. We examined how the use of urban, coastal, and offshore habitats influenced spatiotemporal predictability in the foraging patterns of herring gulls (Larus argentatus) and great black-backed gulls (L. marinus). Since gulls show higher site fidelity when foraging in urban habitats, we predicted that these trips would also show higher route fidelity. Similarly, we predicted that gulls foraging in coastal habitats would adapt the timing of foraging trips relative to tides.
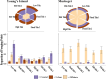
Methods: We analyzed GPS tracks of herring gulls (n = 79) and great black-backed gulls (n = 37)-between 2016-2022 from four nesting colonies whose surrounding areas varied in their degree of urbanization. Fréchet distance, which is defined as the repeated use of the same path while traveling, was used to assess route fidelity, within colonies and between habitat types. We also compared the consistency of foraging trip timing relative to tidal stage and day of week, respectively, across habitat types.
Results: Neither herring nor great black-backed gulls showed higher route fidelity in urban habitats. Herring gulls showed direct travel between urban foraging sites but revisited sites in different orders, suggesting that a mosaic map may be used to navigate between known urban foraging sites. Herring and great black-backed gulls that foraged at coastal sites exhibited patterns in trip timing in relation to the tidal cycle, with foraging primarily occurring at or around low tide. Herring gulls in urban environments foraged more on Fridays and weekends, possibly due to increased or altered human activities on these days.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate the importance of spatial memory and spatiotemporal predictability of gull foraging habitats and highlight the extent to which gulls adjust their movements based on their foraging habitats.
Keywords: Larus argentatus; Larus marinus; Fréchet distance; GPS tracking; Great black-backed gull; Herring gull; Route fidelity; Seabirds; Tidal patterns.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal handling and sampling were approved by Stony Brook University’s institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC number 875550). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Closely related gull species show contrasting foraging strategies in an urban environment.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 8;11(1):23619. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02821-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34880306 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of urbanization on the foraging ecology and microbiota of the generalist seabird Larus argentatus.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 18;13(12):e0209200. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209200. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30562368 Free PMC article.
-
Herring gulls and great black-backed gulls as indicators of contaminants in bald eagles in Lake Ontario, Canada.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2002 May;21(5):1015-25. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12013123
-
Population-level plasticity in foraging behavior of western gulls (Larus occidentalis).Mov Ecol. 2017 Dec 19;5:27. doi: 10.1186/s40462-017-0118-9. eCollection 2017. Mov Ecol. 2017. PMID: 29270295 Free PMC article.
-
Intercolony variations in movement patterns and foraging behaviors among herring gulls (Larus argentatus) breeding in the eastern Wadden Sea.Ecol Evol. 2018 Jul 6;8(15):7529-7542. doi: 10.1002/ece3.4167. eCollection 2018 Aug. Ecol Evol. 2018. PMID: 30151168 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Able KP. The concepts and terminology of bird navigation. J Avian Biol. 2001;32(2):174–83.
-
- Agostinelli C and Lund U. R package 'circular': Circular Statistics (version 0.5–0). 2023. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=circular
-
- Alldredge AL, Hamner WM. Recurring aggregation of zooplankton by a tidal current. Estuar Coast Mar Sci. 1980;10(1):31–7.
-
- Alerstam T, Hake M, Kjellén N. Temporal and spatial patterns of repeated migratory journeys by ospreys. Anim Behav. 2006;71(3):555–66.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

