Predicting abatacept retention using machine learning
- PMID: 39893489
- PMCID: PMC11786492
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-025-03484-0
Predicting abatacept retention using machine learning
Abstract
Background: The incorporation of machine learning is becoming more prevalent in the clinical setting. By predicting clinical outcomes, machine learning can provide clinicians with a valuable tool for refining precision medicine approaches and improving treatment outcomes.
Methods: This was a post hoc analysis of pooled patient-level data from the global, real-world ACTION and ASCORE trials in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) initiating abatacept. Patient demographic and disease characteristics were input across 10 machine learning models used to predict 12-month treatment retention. Retention was defined as treatment for > 365 days or ≤ 365 days in patients who achieved remission or major clinical response (based on European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology response criteria). The pooled dataset was split into a training/validation cohort for model development and a test cohort for an unbiased evaluation of performance. SHapley Additive exPlanation (SHAP) values determined the level of importance and directionality for key patient features predicting abatacept retention.
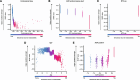
Results: The pooled ACTION and ASCORE dataset included 5320 patients with RA (mean [standard deviation] age 57.7 [12.7] years; 79% female). The 12-month abatacept retention rate was 61% (n = 3236) with a discontinuation rate of 39% (n = 2037). In the training set (n = 4218), the gradient-boosting classifier model demonstrated the best performance (testing accuracy: 62%). This model had an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (95% confidence interval) of 0.620 (0.586, 0.653) and F1 score of 0.659 (0.625, 0.689) in the test set of patients (n = 1055). Using this model, the five most important variables predicting 12-month abatacept retention were low body mass index (BMI), low American College of Rheumatology functional status class, anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) positivity, low Patient Global Assessment, and younger age.
Conclusions: The gradient-boosting classifier model identified key patient features predictive of abatacept retention from this large, real-world study population. The SHAP values conveyed the directionality and importance of BMI, functional status, ACPA serostatus, Patient Global Assessment, and age for abatacept retention. Findings are consistent with previous observations and help validate the machine learning approach for predictive modelling in RA treatment, and may help inform clinical decision making.
Trial registration: NCT02109666 (ACTION), NCT02090556 (ASCORE).
Keywords: Abatacept; Machine learning; Retention; Rheumatoid arthritis; Treatment response.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was conducted in accordance with International Society for Pharmacoepidemiology Guidelines for Good Pharmacoepidemiology Practices [20] and applicable regulatory requirements. The ACTION and ASCORE study protocols and patient enrolment materials were approved according to local law in each participating country prior to initiation of each study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: RA: advisory role: AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche. CBe: former consultant: Bristol Myers Squibb. PM, EA: nothing to disclose. VV-M, AO, GL: employee: Bristol Myers Squibb. SEC, KL: employee, shareholder: Bristol Myers Squibb. AN: advisory role: Bristol Myers Squibb, UCB; speaker/honoraria: Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Roche, UCB; grant/research support: Novartis, AstraZeneca. P-AJ: consultant: Bristol Myers Squibb; speaker/honoraria: AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim. AR: employee, shareholder: Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb (at the time of analysis); shareholder: Genmab. Current affiliation: Eli Lilly & Co. YE: consultant: Bristol Myers Squibb.
Figures



References
-
- Bristol Myers Squibb. Orencia (abatacept) prescribing information. 2024.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

