Epigene functional diversity: isoform usage, disordered domain content, and variable binding partners
- PMID: 39893491
- PMCID: PMC11786378
- DOI: 10.1186/s13072-025-00571-z
Epigene functional diversity: isoform usage, disordered domain content, and variable binding partners
Abstract
Background: Epigenes are defined as proteins that perform post-translational modification of histones or DNA, reading of post-translational modifications, form complexes with epigenetic factors or changing the general structure of chromatin. This specialized group of proteins is responsible for controlling the organization of genomic DNA in a cell-type specific fashion, controlling normal development in a spatial and temporal fashion. Moreover, mutations in epigenes have been implicated as causal in germline pediatric disorders and as driver mutations in cancer. Despite their importance to human disease, to date, there has not been a systematic analysis of the sources of functional diversity for epigenes at large. Epigenes' unique functions that require the assembly of pools within the nucleus suggest that their structure and amino acid composition would have been enriched for features that enable efficient assembly of chromatin and DNA for transcription, splicing, and post-translational modifications.
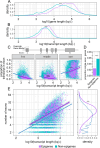
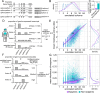
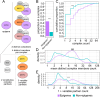
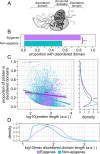
Results: In this study, we assess the functional diversity stemming from gene structure, isoforms, protein domains, and multiprotein complex formation that drive the functions of established epigenes. We found that there are specific structural features that enable epigenes to perform their variable roles depending on the cellular and environmental context. First, epigenes are significantly larger and have more exons compared with non-epigenes which contributes to increased isoform diversity. Second epigenes participate in more multimeric complexes than non-epigenes. Thirdly, given their proposed importance in membraneless organelles, we show epigenes are enriched for substantially larger intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs). Additionally, we assessed the specificity of their expression profiles and showed epigenes are more ubiquitously expressed consistent with their enrichment in pediatric syndromes with intellectual disability, multiorgan dysfunction, and developmental delay. Finally, in the L1000 dataset, we identify drugs that can potentially be used to modulate expression of these genes.
Conclusions: Here we identify significant differences in isoform usage, disordered domain content, and variable binding partners between human epigenes and non-epigenes using various functional genomics datasets from Ensembl, ENCODE, GTEx, HPO, LINCS L1000, and BrainSpan. Our results contribute new knowledge to the growing field focused on developing targeted therapies for diseases caused by epigene mutations, such as chromatinopathies and cancers.
Keywords: Chromatin modifiers; Epigenes; Epigenetics; Rare diseases; Transcriptomics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The omics era: a nexus of untapped potential for Mendelian chromatinopathies.Hum Genet. 2024 Apr;143(4):475-495. doi: 10.1007/s00439-023-02560-2. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 37115317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ASXL1 truncating variants in BOS and myeloid leukemia drive shared disruption of Wnt-signaling pathways but have differential isoform usage of RUNX3.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Nov 29;17(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-02039-7. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39614348 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative splicing of intrinsically disordered regions and rewiring of protein interactions.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013 Jun;23(3):443-50. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2013.03.006. Epub 2013 May 22. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 23706950 Review.
-
Disordered domains in chromatin-binding proteins.Essays Biochem. 2019 Apr 23;63(1):147-156. doi: 10.1042/EBC20180068. Print 2019 Apr 23. Essays Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30940742 Review.
-
The Role of Post-Translational Modifications in the Phase Transitions of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 5;20(21):5501. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215501. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31694155 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Davalos V, Esteller M. Cancer epigenetics in clinical practice. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:376–424. - PubMed
-
- Pan Y, Liu G, Zhou F, Su B, Li Y. DNA methylation profiles in cancer diagnosis and therapeutics. Clin Exp Med. 2018;18:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Berdasco M, Esteller M. Clinical epigenetics: seizing opportunities for translation. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20:109–27. - PubMed

