Regorafenib as a potential drug for severe COVID-19: inhibition of inflammasome activation in mice
- PMID: 39895416
- PMCID: PMC11891780
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.70002
Regorafenib as a potential drug for severe COVID-19: inhibition of inflammasome activation in mice
Abstract
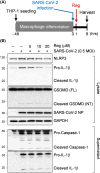
SARS-CoV-2 infection can lead to severe COVID-19, particularly in elderly individuals and those with compromised immunity. Cellular senescence has been implicated as a key pathogenic mechanism. This study investigated the therapeutic potential of regorafenib, a previously characterized senomorphic drug, for severe COVID-19. SARS-CoV-2 virus-infected K18-hACE2 mice, overexpressing the human ACE2 receptor, exhibited 100% mortality by 10 days post infection. Regorafenib treatment significantly improved survival rates, approximately 43% remaining alive. Mechanistically, regorafenib effectively suppressed type I and II interferon and cytokine signaling. Notably, regorafenib inhibited NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation, a key driver of the cytokine storm associated with severe COVID-19. Our findings elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying therapeutic effects of regorafenib and suggest its potential use as a promising treatment option for severe COVID-19.
Keywords: K18‐hACE2; SARS‐CoV‐2; infection; inflammasome; regorafenib.
© 2025 The Author(s). FEBS Open Bio published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The NLRP3 inflammasome and COVID-19: Activation, pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021 Oct;61:2-15. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2021.06.002. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021. PMID: 34183243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 drives NLRP3 inflammasome activation in human microglia through spike protein.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Jul;28(7):2878-2893. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01831-0. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36316366 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of sEH inhibition on the eicosanoid and cytokine storms in SARS-CoV-2-infected mice.FASEB J. 2024 May 31;38(10):e23692. doi: 10.1096/fj.202302202RR. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 38786655 Free PMC article.
-
Specific inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome suppresses immune overactivation and alleviates COVID-19 like pathology in mice.EBioMedicine. 2022 Jan;75:103803. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103803. Epub 2021 Dec 31. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 34979342 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Severe COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 23;11:1518. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01518. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32655582 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

