Combinatorial immunotherapy with anti-ROR1 CAR NK cells and an IL-21 secreting oncolytic virus against neuroblastoma
- PMID: 39895691
- PMCID: PMC11783442
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200927
Combinatorial immunotherapy with anti-ROR1 CAR NK cells and an IL-21 secreting oncolytic virus against neuroblastoma
Abstract
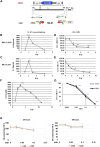
Children with recurrent/metastatic neuroblastoma (NB) have a dismal survival (<25%). Novel therapies are desperately needed. Receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (ROR1) is highly expressed on NB. C021 is a selective oncolytic herpes simplex virus modified to overexpress human interleukin-21 (hIL-21), a cytokine that enhances natural killer (NK) cell cytotoxicity. In the current study, we successfully engineered ex-vivo-expanded NK cells to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) against ROR1 using mRNA electroporation and investigated the efficacy of anti-ROR1-CAR-NK cells combined with C021 in targeting ROR1+ NB. We found that C021-infected NB cells secreted hIL-21 in vitro and in vivo. Compared to the non-cytokine-secreting parental virus C134, C021 significantly enhanced the in vitro cytotoxicity (p < 0.05) of anti-ROR1-CAR-NK cells with increased interferon (IFN)-γ (p < 0.05), granzyme B (p < 0.05), and perforin (p < 0.05) secretion against NB cells. Furthermore, the combination of C021 and anti-ROR1-CAR-NK cells significantly extended the survival of human NB xenografted NSG mice compared to controls (mock NK, ROR1-CAR-NK, C134, C021, C134+ROR1-CAR-NK, and C021+mock NK). Our results suggest that cytokine-secreting oncolytic virus in combination with CAR-NK cells is a novel, effective immunotherapeutic approach for high-risk NB.
Keywords: CAR; IL-21; ROR1; chimeric antigen receptor; interleukin-21; natural killer cells; neuroblastoma; oncolytic herpes simplex virus.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was presented in part at the Pediatric Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Consortium (2023), Fort Worth, TX; International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy (2022), San Francisco, CA; and Transplantation & Cellular Therapy Meetings of the American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (2022), Salt Lake City, Utah. M.S.C. has served as a consultant for Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Omeros Pharmaceuticals, Servier Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, and Novartis Pharmaceuticals; on speakers bureau for Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Servier Pharmaceuticals, Amgen, Inc., Sanofi, and Sobi; and on the advisory board for Astra Zeneca and has received research funding from Celularity, Merck, Miltenyi Biotec, Servier, Omeros, Jazz, and Janssen. D.A.L. reports personal fees and other fees from Kiadis Pharma, CytoSen Therapeutics, Courier Therapeutics, and Caribou Biosciences outside the submitted work. In addition, D.A.L. has a patent broadly related to NK cell therapy of cancer with royalties paid to Kiadis Pharma. T.P.C. recently served as a one-time consultant to Blueprint, Incyte, and Oncopeptides and a DSMB chair for SpringWorks and is a cofounder of Vironexis Biotherapeutics, Inc.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
