Facile Sol-Gel Synthesis of C, N Codoped-TiO2 for Efficient Degradation of Palm Oil Mill Effluent
- PMID: 39895745
- PMCID: PMC11780434
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c08813
Facile Sol-Gel Synthesis of C, N Codoped-TiO2 for Efficient Degradation of Palm Oil Mill Effluent
Abstract
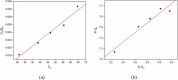
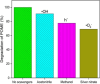
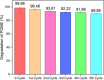
Wastewater treatment has been regarded as an effective solution in lowering the potential environmental hazards caused by palm oil mill effluent (POME). To ensure the efficient remediation of POME, the implementation of a promising strategy is necessary to overcome the limitations of conventional water treatment methods for the treatment of this pollutant. In this study, the synthesis of carbon, nitrogen codoped titanium dioxide nanoparticles (C, N-TiO2 NPs) was successfully performed by a sol-gel approach for the treatment of POME as a model pollutant under solar light irradiation. The synthesized C, N-TiO2 NPs displayed unique characteristics including an anatase phase with an average crystallite size of 11.35 nm and irregular spherical structures. Additionally, C, N-TiO2 possessed a lower band gap energy of 2.95 eV than 3.2 V of bulk anatase TiO2 and slower electron-hole (e--h+) pair recombination rate as evidenced by photoluminescence (PL) studies. The adsorption isotherm study of POME was most compatible with the Langmuir isotherm model, and the POME degradation kinetics proceeded according to first-order kinetics. Accordingly, the photocatalytic degradation of POME displayed a maximum degradation efficiency of 100% under the optimum condition of pH 7 in the presence of 0.12 g of the C, N-TiO2 photocatalyst within 150 min. The scavenging study showed that the superoxide radical (•O2 -) was the primary active species in the POME photodegradation. Finally, the reusability analysis confirmed that the C, N-TiO2 NPs could be reused for a maximum of five cycles, making them promising photocatalysts for wastewater treatment.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures









References
-
- Madhav S.; Ahamad A.; Singh A. K.; Kushawaha J.; Chauhan J. S.; Sharma S.; Singh P.. Water Pollutants: Sources and Impact on the Environment and Human Health. In Sensors in Water Pollutants Monitoring: Role of Material Pooja D.; Kumar P.; Singh P., Patil S. (Eds.); Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp 43–62.
-
- Lok X.; Chan Y. J.; Foo D. C. Y. Simulation and optimization of full-scale palm oil mill effluent (POME) treatment plant with biogas production. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 10155810.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101558. - DOI
-
- Mohd Yusof M. A. B.; Chan Y. J.; Chong C. H.; Chew C. L. Effects of operational processes and equipment in palm oil mills on characteristics of raw Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME): A comparative study of four mills. Clean. Waste Syst. 2023, 5, 10010110.1016/j.clwas.2023.100101. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
