Jellyfish Collagen Grafted with Hydroxybutyl Chitosan and Protocatechuic Acid Adhesive Sponge with Antibacterial Activity for Rapid Hemostasis
- PMID: 39895763
- PMCID: PMC11780408
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c06103
Jellyfish Collagen Grafted with Hydroxybutyl Chitosan and Protocatechuic Acid Adhesive Sponge with Antibacterial Activity for Rapid Hemostasis
Abstract
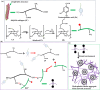
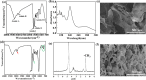
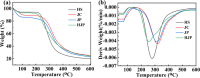
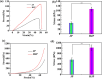
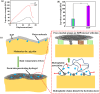
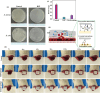
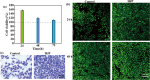
Natural jellyfish collagen (JC) has garnered significant attention in the field of hemostasis due to its oceanic origin, nontoxicity, biodegradability, and absence of complications related to diseases and religious beliefs. However, the hemostatic performance of pure JC is limited by its poor stability, adhesion to wet tissue, and mechanical properties. We developed a novel (HJP) sponge comprising JC, protocatechuic acid (PA), and hydroxybutyl chitosan (HS) to enhance the application of JC in emergency hemostasis. This sponge exhibits antibacterial properties, good biocompatibility, wet tissue adhesion, and hemostatic capabilities. The HJP sponge demonstrates excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength (tensile strength: ∼106.6 kPa, compressive strength at 70% compressive strain: ∼1013.5 kPa) and strong wet tissue adhesion (∼117.1 kPa). Upon application to a wound, the HJP sponge rapidly forms a wound seal, achieving effective hemostasis through the synergistic action of PA and JC. The blood loss was also reduced to 0.105 g when compared to a commercial gelatin sponge. This JC-based sponge, with its multifaceted characteristics, holds significant promise for rapid hemostasis in clinical applications.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Xia Y.; Yang R.; Wang H.; Li Y.; Fu C. Application of chitosan-based materials in surgical or postoperative hemostasis. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 994265 10.3389/fmats.2022.994265. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
