Global research progress and trends in traditional Chinese medicine for chronic kidney disease since the 21st century: a bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 39895816
- PMCID: PMC11782275
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1480832
Global research progress and trends in traditional Chinese medicine for chronic kidney disease since the 21st century: a bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Objective: This study analyzed literature on traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in treating chronic kidney disease (CKD) to identify research trends and provide guidance for future studies and clinical practice.
Methods: The study used data from Web of Science from 2000 to 2024 to analyze English-language literature on CKD and TCM. Bibliometric analysis was done using R software and the bibliometric package, with scientific mapping and visualization analysis conducted using tools like Citespace, VOSviewer, and ScimagoGraphica to explore research trends and connections.
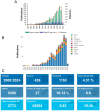
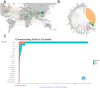
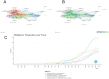
Results: This study revealed that a total of 1,153 relevant documents were retrieved, and the number of published articles showed an increasing trend, reaching a peak in 2022. In terms of article publication, China ranked first with 760 articles, closely followed by the United States with 132 articles. Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine published 60 papers, the most among academic institutions, followed by Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine with 54 papers. In terms of individual authors, Liu Xinhui holds the record for the highest number of published articles, totaling 17, followed by Li Ping and Li Shunmin. The prevalent keywords include "chronic kidney disease," "TCM," and "oxidative stress." Currently, the prominent areas of research interest include network pharmacology, gut microbiota, oxidative stress, and related topics. The current research trend in this field is towards the adoption of novel methodologies such as network pharmacology and the emphasis on exploring the relationship between gut microbiota and CKD.
Conclusion: Global research on TCM in the treatment of CKD is showing a positive development trend, but further research on safety, efficacy evaluation, and international cooperation is still needed. The development trend is to adopt new scientific research methods and focus on exploring the mechanism of TCM in treating CKD.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; gut microbiota; network pharmacology; oxidative stress; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Wang, Chen, Yang and Xiong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

