Prevalence and molecular characterization of hepatitis delta virus infection among hepatitis B virus surface antigen positive students and pregnant women in N'djamena, Chad
- PMID: 39895833
- PMCID: PMC11786080
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2024.100560
Prevalence and molecular characterization of hepatitis delta virus infection among hepatitis B virus surface antigen positive students and pregnant women in N'djamena, Chad
Abstract
Objectives: This study sought to determine the prevalence of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-hepatitis D virus (HDV) co-infection and to characterize isolates of both viruses in a Chadian population of HBV surface antigen (HBsAg)-positive pregnant women and students.
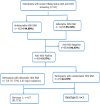
Methods: This was a cross-sectional retrospective study using archived samples from pregnant women and students in N'djamena who had been systematically screened for HBsAg between April and August 2021. HBsAg-positive samples were tested for the presence of HDV antibodies (Ab) and were screened for the presence of both HBV and HDV (in anti-HDV Ab-positive samples) viral load estimations. Genome sequencing of the viruses was used for both genotyping and phylogenetic analysis.
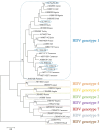
Results: A total of 94 participants were included in this study. The mean age was 24 ± 4.89 years (range: 18-42 years). Anti-HDV Ab were found in 9.57% (9/94) of the participants. The prevalence of anti-HDV Ab positivity among students (6.45% [4/62]) was lower than the 15.63% (5/32) observed among pregnant women. HDV-RNA was detected in 7/9 (77.77%) confirmed anti-HDV-positive participants. Most HDV-RN-positive participants had very low HBV DNA viral loads. All HBV sequences belonged to genotype E and all HDV sequences to genotype 1.
Conclusions: Hepatitis D is a potential public health challenge in Chad, which requires active surveillance and public education in the country for proper control. This surveillance should be supported with mass immunization against HBV.
Keywords: Chad and Africa; Genotype; Hepatitis D virus; Pregnant women; Prevalence; Students.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous