SiRNA-mediated Silencing of the RPS19 Gene Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Cell Cycle Progression in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells
- PMID: 39895916
- PMCID: PMC11786124
- DOI: 10.22088/IJMCM.BUMS.13.4.436
SiRNA-mediated Silencing of the RPS19 Gene Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Cell Cycle Progression in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells
Abstract
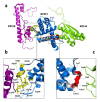
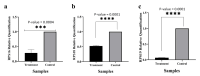
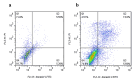
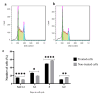
This research delves into the therapeutic implications of utilizing small interfering RNA (siRNA) to target the ribosomal protein S19 (RPS19) gene in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) using the K562 cell line model. The primary objective was to investigate how gene silencing affects apoptosis promotion and cell cycle arrest. The study employed bioinformatics tools and databases to explore the interactions involving RPS19 and neighboring proteins. Subsequently, siRNA-mediated gene silencing was utilized to suppress RPS19 expression in K-562 cells, with assessments conducted on cell cycle progression and apoptosis through flow cytometry analysis. Furthermore, real-time PCR was employed to evaluate the expression levels of RPS19, along with the closely associated RPS16 and RPS18 genes. Silencing the RPS19 gene in siRNA-transfected K-562 cells led to an increase in apoptotic cells by over 20%, with a significant accumulation in the sub-G1 and G1 phases. Additionally, the knockdown of RPS19 resulted in a 75% decrease in RPS16 expression and a 50% decrease in RPS18 expression. These results demonstrate the therapeutic potential of targeting RPS19 in CML cells, suggesting a promising approach for precise treatment strategies in leukemia and potentially other types of cancer.
Keywords: RPS19; apoptosis; cell cycle; chronic myeloid leukemia; gene silencing; siRNA.
© The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rana A, Hussain Shah S, Rehman N, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia: Attributes of break point cluster region-abelson (BCR-ABL) J Cancer Res Exp Oncol. 2011;3:62–6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
