Endophytic Fungi Isolated from the Marine Macroalga Dictyopteris pacifica in Korea
- PMID: 39895928
- PMCID: PMC11780697
- DOI: 10.1080/12298093.2024.2440975
Endophytic Fungi Isolated from the Marine Macroalga Dictyopteris pacifica in Korea
Abstract
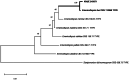
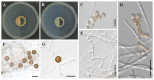
The exploration of endophytic fungi associated with seaweeds has garnered significant interest due to their crucial ecological functions and potential as sources of valuable bioactive compounds. In this study, we isolated and identified endophytic fungi from the brown seaweed Dictyopteris pacifica, collected from the intertidal zone of Yeongdoek, Gyeongsangbuk-do in Korea. Through morphological examination and molecular phylogenetic analysis using multiple molecular markers, including ITS, LSU, SSU, TEF1, TUB2, and RPB2 sequences, we identified three fungal species not previously recorded in Korea: Emericellopsis fuci, Neoarthrinium lithocarpicola, and Periconia chimonanthi. Detailed descriptions of morphological characteristics and phylogenetic analyses are provided. This study represents the first report of these endophytic fungi isolated from D. pacifica in Korea, thereby enhancing the understanding of the diversity of seaweed-associated endophytic fungi in the region.
Keywords: Dictyopteris pacifica; endophytic fungi; macro algae; seaweed.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group on behalf of the Korean Society of Mycology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Morphological and Phylogenetic Characterization of Endophytic Fungi Isolated from Brown Algae (Phaeophyceae) in Korea.Mycobiology. 2025 Aug 7;53(5):620-628. doi: 10.1080/12298093.2025.2535776. eCollection 2025. Mycobiology. 2025. PMID: 40792186 Free PMC article.
-
Marine seaweed endophytic fungi-derived active metabolites promote reactive oxygen species-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human breast cancer cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 May 5;51(1):611. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09511-8. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38704796
-
Protoplast isolation from Dictyopteris pacifica and Scytosiphon lomentaria, using a simple commercial enzyme preparation.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2021 Sep 3;19(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s43141-021-00226-y. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34477994 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity, Distribution, and Host Plant of Endophytic Fungi: A Focus on Korea.Mycobiology. 2022 Dec 17;50(6):399-407. doi: 10.1080/12298093.2022.2154044. eCollection 2022. Mycobiology. 2022. PMID: 36721791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antitumor Potential of Seaweed Derived-Endophytic Fungi.Antibiotics (Basel). 2019 Oct 31;8(4):205. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics8040205. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31683523 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microascus microspora sp. nov. and Tolypocladium terrae sp. nov.; Two Novel Fungal Species Isolated from Soil in Korea.Mycobiology. 2025 Mar 17;53(3):280-288. doi: 10.1080/12298093.2025.2474291. eCollection 2025. Mycobiology. 2025. PMID: 40103852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee JW, Hwang IK.. Dictyotales, Desmarestiales. In: Boo SM, editor. Algal flora of Korea. Marine Brown Algae II, Heterokontophyta: Phaeophyceae: Ishigeales, Dictyotales, Desmarestiales, Sphacelariales, Cutleriales, Ralfisales, Laminariales. Incheon: National Institute of Biological Resources; 2010. p. 19–69.
-
- Nisizawa K. Pharmaceutical studies on marine algae of Japan. In: Hoppe HA, Levring T, Tanaka Y, editors. Marine algae in pharmaceutical science. Berlin/New York: Walter de Gruyter; 1979. p. 243–266.
-
- Zatelli GA, Philippus AC, Falkenberg M.. An overview of odoriferous marine seaweeds of the Dictyopteris genus: insights into their chemical diversity, biological potential and ecological roles. Revista Brasileira Farmacognos. 2018;28(2):243–260. doi: 10.1016/j.bjp.2018.01.005. - DOI
-
- Petrini O. Fungal endophytes of tree leaves. In: Andrews JH, Hirano SS, editors. Microbial ecology of leaves. New York: Springer; 1991. p. 179–197.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
