The role of Bacillus species in the management of plant-parasitic nematodes
- PMID: 39895938
- PMCID: PMC11782231
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1510036
The role of Bacillus species in the management of plant-parasitic nematodes
Abstract
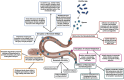
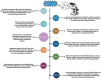
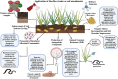
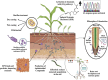
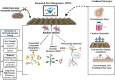
Plant-parasitic nematodes (PPNs), including root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.), cyst nematodes (Heterodera and Globodera spp.), and other economically significant nematode species, pose severe threats to global agriculture. These nematodes employ diverse survival strategies, such as dormancy in cysts or robust infective juvenile stages. Consequently, their management is challenging. Traditional control methods, such as the use of chemical nematicides, are increasingly scrutinized because of environmental and health concerns. This review focuses on the specific mechanisms employed by Bacillus spp., including nematicidal compound production, systemic resistance induction, and cuticle degradation, to target root-knot and cyst nematodes. These mechanisms offer sustainable solutions for managing nematodes and promoting soil health by enhancing microbial diversity and nutrient cycling. An integrated approach leveraging Bacillus-based biocontrol is proposed to maximize efficacy and agricultural sustainability.
Keywords: Bacillus spp.; biocontrol; integrated pest management; nematicidal compounds; plant-parasitic nematodes.
Copyright © 2025 Vasantha-Srinivasan, Park, Kim, Jung and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
KP was the CEO of Invirustech Co., Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Aballay E., Prodan S., Correa P., Allende J. (2020). Assessment of rhizobacterial consortia to manage plant parasitic nematodes of grapevine. Crop Prot. 131:105103. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2020.105103 - DOI
-
- Abd-Elgawad M. M., Askary T. H. (2018). Fungal and bacterial nematicides in integrated nematode management strategies. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 28, 1–24. doi: 10.1186/s41938-018-0080-x, PMID: - DOI
-
- Abd-Elgawad M. M. M., Askary T. H. (2020). Factors affecting success of biological agents used in controlling the plant-parasitic nematodes. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 30:17. doi: 10.1186/s41938-020-00215-2 - DOI
-
- Abdellatif A. A., Tahany A. R., Sayed M. A., Dina I., Elmaghraby M. M. K. (2021). Activity of Serratia spp. and Bacillus spp. as biocontrol agents against Meloidogyne incognita infecting tomato. Pakist. J. Biotechnol. 18, 37–47. doi: 10.34016/pjbt.2021.18.2/3.37 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

