Case Report: Successful treatment of metastatic retinoblastoma with CNS involvement with anti-GD2 immunotherapy, intrathecal topotecan and reduced systemic chemotherapy
- PMID: 39895987
- PMCID: PMC11782212
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2024.1509645
Case Report: Successful treatment of metastatic retinoblastoma with CNS involvement with anti-GD2 immunotherapy, intrathecal topotecan and reduced systemic chemotherapy
Abstract
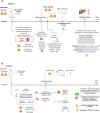
High-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell rescue has improved outcomes in patients with metastatic retinoblastoma (RB). Despite significant advances, acute and long-term side-effects, particularly in visually impaired and cancer-predisposed patients, underscore the need for additional treatment options. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) directed against the tumor-associated antigen GD2 are of considerable interest. Additional lines of RB research include tracking minimal disseminated disease (MDD) to permit timely intervention in patients with CNS metastasis. We present two cases of bilateral, metastatic RB, managed with the anti-GD2 mAb naxitamab following reduced intensity myeloablative chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) with intrathecal topotecan for MDD detected in the CSF. The patients remain disease-free 10 and 9 years after initial diagnosis. While additional studies are needed, the results suggest anti-GD2 mAbs and CNS-directed chemotherapy may improve long-term outcomes and reduce cytotoxicity for high-risk patients with RB.
Keywords: GD2; anti-GD2 immunotherapy; intrathecal topotecan; metastatic retinoblastoma; naxitamab.
© 2025 Larrosa, Simao-Rafael, Salvador, Muñoz, Lavarino, Chantada and Mora.
Conflict of interest statement
JM Consulting fees from Y-mAbs Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted therapies in retinoblastoma: GD2-directed immunotherapy following autologous stem cell transplantation and evaluation of alternative target B7-H3.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024 Jan 19;73(1):19. doi: 10.1007/s00262-023-03587-0. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38240863 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation in High-Risk Neuroblastoma Consolidated by anti-GD2 Immunotherapy. Results of Two Consecutive Studies.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Oct 30;11:575009. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.575009. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33324208 Free PMC article.
-
The GD2-specific 14G2a monoclonal antibody induces apoptosis and enhances cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs in IMR-32 human neuroblastoma cells.Cancer Lett. 2009 Aug 28;281(2):171-82. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.02.040. Epub 2009 Mar 31. Cancer Lett. 2009. PMID: 19339105
-
Survival Benefit of Myeloablative Therapy with Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation in High-Risk Neuroblastoma: A Systematic Literature Review.Target Oncol. 2024 Mar;19(2):143-159. doi: 10.1007/s11523-024-01033-4. Epub 2024 Feb 24. Target Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38401028 Free PMC article.
-
Naxitamab: a humanized anti-glycolipid disialoganglioside (anti-GD2) monoclonal antibody for treatment of neuroblastoma.Drugs Today (Barc). 2021 Nov;57(11):677-688. doi: 10.1358/dot.2021.57.11.3343691. Drugs Today (Barc). 2021. PMID: 34821881 Review.
Cited by
-
Update on Retinoblastoma Therapies.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jul 4;61(7):1219. doi: 10.3390/medicina61071219. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40731848 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cheung NK V, Cheung IY, Kushner BH, Ostrovnaya I, Chamberlain E, Kramer K, et al. Murine anti-GD2 monoclonal antibody 3F8 combined with granulocyte- macrophage colony-stimulating factor and 13-cis-retinoic acid in high-risk patients with stage 4 neuroblastoma in first remission. J Clin Oncol. (2012) 30(26):3264–70. 10.1200/JCO.2011.41.3807 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources