Deep gradient reinforcement learning for music improvisation in cloud computing framework
- PMID: 39896013
- PMCID: PMC11784531
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2265
Deep gradient reinforcement learning for music improvisation in cloud computing framework
Abstract
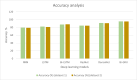
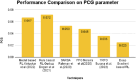
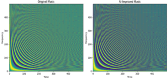
Artificial intelligence (AI) in music improvisation offers promising new avenues for developing human creativity. The difficulty of writing dynamic, flexible musical compositions in real time is discussed in this article. We explore using reinforcement learning (RL) techniques to create more interactive and responsive music creation systems. Here, the musical structures train an RL agent to navigate the complex space of musical possibilities to provide improvisations. The melodic framework in the input musical data is initially identified using bi-directional gated recurrent units. The lyrical concepts such as notes, chords, and rhythms from the recognised framework are transformed into a format suitable for RL input. The deep gradient-based reinforcement learning technique used in this research formulates a reward system that directs the agent to compose aesthetically intriguing and harmonically cohesive musical improvisations. The improvised music is further rendered in the MIDI format. The Bach Chorales dataset with six different attributes relevant to musical compositions is employed in implementing the present research. The model was set up in a containerised cloud environment and controlled for smooth load distribution. Five different parameters, such as pitch frequency (PF), standard pitch delay (SPD), average distance between peaks (ADP), note duration gradient (NDG) and pitch class gradient (PCG), are leveraged to assess the quality of the improvised music. The proposed model obtains +0.15 of PF, -0.43 of SPD, -0.07 of ADP and 0.0041 NDG, which is a better value than other improvisation methods.
Keywords: Cloud frameworks; Containerization; Gated recurrent units; Music improvisation; Reinforcement learning.
©2025 Alrowais et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ban Y, Liu Y, Yin Z, Liu X, Liu M, Yin L, Li X, Zheng W. Micro-directional propagation method based on user clustering. Computing and Informatics. 2023;42(6):1445–1470. doi: 10.31577/cai_2023_6_1445. - DOI
-
- Bell C. Algorithmic music composition using dynamic Markov chains and genetic algorithms. Journal of Computing Sciences in Colleges. 2011;27(2):99–107. doi: 10.5555/2038836.2038850. - DOI
-
- Carnovalini F, Rodà A. A multilayered approach to automatic music generation and expressive performance. 2019 international workshop on multilayer music representation and processing (MMRP); Piscataway. 2019. pp. 41–48. - DOI
-
- Chen H, Xiao Q, Yin X. 2019. Generating music algorithm with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. 2019 IEEE 2nd international conference on electronics technology (ICET); Piscataway. 2019. pp. 576–580. - DOI
-
- Dai C. Design of an improvisational singing training system based on machine learning algorithms. International conference on cognitive based information processing and applications; Cham. 2023. pp. 213–221. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
