Cervical mucus in linked human Cervix and Vagina Chips modulates vaginal dysbiosis
- PMID: 39896100
- PMCID: PMC11779628
- DOI: 10.1038/s44294-025-00054-2
Cervical mucus in linked human Cervix and Vagina Chips modulates vaginal dysbiosis
Abstract
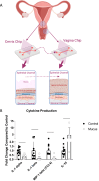
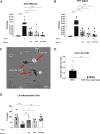
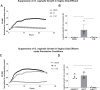
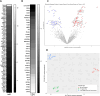
This study explores the protective role of cervicovaginal mucus in maintaining vaginal health, particularly in relation to bacterial vaginosis (BV), using organ chip technology. By integrating human Cervix and Vagina Chips, we demonstrated that cervical mucus significantly reduces inflammation and epithelial damage caused by a dysbiotic microbiome commonly associated with BV. Proteomic analysis of the Vagina Chip, following exposure to mucus from the Cervix Chip, revealed differentially abundant proteins, suggesting potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for BV management. Our findings highlight the essential function of cervical mucus in preserving vaginal health and underscore the value of organ chip models for studying complex interactions within the female reproductive tract. This research provides new insights into the mechanisms underlying vaginal dysbiosis and opens avenues for developing targeted therapies and diagnostic tools to enhance women's reproductive health.
Keywords: Physiology; Reproductive biology.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsD.E.I. is a founder, board member, and chairs the SAB of Emulate Inc., in which he also holds equity. The author O.G., A.G., Z.I., A.S., H.R., J.C., B.B., S.S., G.G., and A.J. report no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- McLoughlin, K. et al. Host selection of microbiota via differential adhesion. Cell Host Microbe19, 550–559 (2016). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
