PhosNetVis: A web-based tool for fast kinase-substrate enrichment analysis and interactive 2D/3D network visualizations of phosphoproteomics data
- PMID: 39896259
- PMCID: PMC11783894
- DOI: 10.1016/j.patter.2024.101148
PhosNetVis: A web-based tool for fast kinase-substrate enrichment analysis and interactive 2D/3D network visualizations of phosphoproteomics data
Abstract
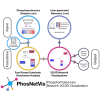
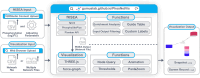
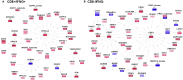
Protein phosphorylation involves the reversible modification of a protein (substrate) residue by another protein (kinase). Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry studies are rapidly generating massive protein phosphorylation datasets across multiple conditions. Researchers then must infer kinases responsible for changes in phosphosites of each substrate. However, tools that infer kinase-substrate interactions (KSIs) are not optimized to interactively explore the resulting large and complex networks, significant phosphosites, and states. There is thus an unmet need for a tool that facilitates user-friendly analysis, interactive exploration, visualization, and communication of phosphoproteomics datasets. We present PhosNetVis, a web-based tool for researchers of all computational skill levels to easily infer, generate, and interactively explore KSI networks in 2D or 3D by streamlining phosphoproteomics data analysis steps within a single tool. PhostNetVis lowers barriers for researchers by rapidly generating high-quality visualizations to gain biological insights from their phosphoproteomics datasets. It is available at https://gumuslab.github.io/PhosNetVis/.
Keywords: 3D visualization; CPTAC; fast kinase-substrate enrichment analysis; interactive visualization; kinase-substrate interaction; network visualization; phosphoproteomics; phosphorylation.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.G. reports other research funding from Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Genentech, Regeneron, and Takeda and consulting for Taiho Pharmaceuticals not related to this study.
Figures


Update of
-
PhosNetVis: A web-based tool for fast kinase-substrate enrichment analysis and interactive 2D/3D network visualizations of phosphoproteomics data.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 18:arXiv:2402.05016v4. ArXiv. 2024. Update in: Patterns (N Y). 2025 Jan 10;6(1):101148. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2024.101148. PMID: 39010877 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Hallal M., Braga-Lagache S., Jankovic J., Simillion C., Bruggmann R., Uldry A.-C., Allam R., Heller M., Bonadies N. Inference of kinase-signaling networks in human myeloid cell line models by Phosphoproteomics using kinase activity enrichment analysis (KAEA) BMC Cancer. 2021;21:789. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08479-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

