This is a preprint.
Cholinergic dynamics in the septo-hippocampal system provide phasic multiplexed signals for spatial novelty and correlate with behavioral states
- PMID: 39896475
- PMCID: PMC11785060
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.01.21.634097
Cholinergic dynamics in the septo-hippocampal system provide phasic multiplexed signals for spatial novelty and correlate with behavioral states
Update in
-
Cholinergic Dynamics in the Septo-hippocampal System Provide Phasic Multiplexed Signals for Spatial Novelty and Correlate with Behavioral States.J Neurosci. 2025 Oct 8;45(41):e0133252025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0133-25.2025. J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40930973 Free PMC article.
Abstract
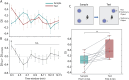
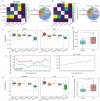
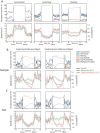
In the hippocampal formation, cholinergic modulation from the medial septum/diagonal band of Broca (MSDB) is known to correlate with the speed of an animal's movements at sub-second timescales and also supports spatial memory formation. Yet, the extent to which sub-second cholinergic dynamics, if at all, align with transient behavioral and cognitive states supporting the encoding of novel spatial information remains unknown. In this study, we used fiber photometry to record the temporal dynamics in the population activity of septo-hippocampal cholinergic neurons at sub-second resolution during a hippocampus-dependent object location memory task using ChAT-Cre mice. Using a general linear model, we quantified the extent to which cholinergic dynamics were explained by changes in movement speed, behavioral states such as locomotion, grooming, and rearing, and hippocampus-dependent cognitive states such as recognizing a novel location of a familiar object. The data show that cholinergic dynamics contain a multiplexed code of fast and slow signals i) coding for the logarithm of movement speed at sub-second timescales, ii) providing a phasic spatial novelty signal during the brief periods of exploring a novel object location, and iii) coding for environmental novelty at a seconds-long timescale. Furthermore, behavioral event-related phasic cholinergic activity around the onset and offset of the behavior demonstrates that fast cholinergic transients help facilitate a switch in cognitive and behavioral state before and during the onset of behavior. These findings enhance understanding of the mechanisms by which cholinergic modulation contributes to the coding of movement speed and encoding of novel spatial information.
Keywords: acetylcholine; encoding and retrieval; fiber photometry; hippocampal formation; medial septum; novel object location.
Figures


References
-
- DATAtab Team (2024). DATAtab: Online Statistics Calculator. DATAtab e.U. Graz, Austria. URL https://datatab.net
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
