This is a preprint.
Generative modeling for RNA splicing predictions and design
- PMID: 39896553
- PMCID: PMC11785043
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.01.20.633986
Generative modeling for RNA splicing predictions and design
Abstract
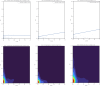
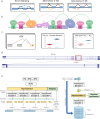
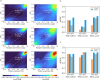
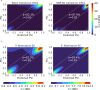
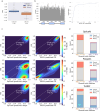
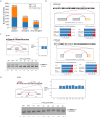
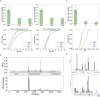
Alternative splicing (AS) of pre-mRNA plays a crucial role in tissue-specific gene regulation, with disease implications due to splicing defects. Predicting and manipulating AS can therefore uncover new regulatory mechanisms and aid in therapeutics design. We introduce TrASPr+BOS, a generative AI model with Bayesian Optimization for predicting and designing RNA for tissue-specific splicing outcomes. TrASPr is a multi-transformer model that can handle different types of AS events and generalize to unseen cellular conditions. It then serves as an oracle, generating labeled data to train a Bayesian Optimization for Splicing (BOS) algorithm to design RNA for condition-specific splicing outcomes. We show TrASPr+BOS outperforms existing methods, enhancing tissue-specific AUPRC by up to 2.4 fold and capturing tissue-specific regulatory elements. We validate hundreds of predicted novel tissue-specific splicing variations and confirm new regulatory elements using dCas13. We envision TrASPr+BOS as a light yet accurate method researchers can probe or adopt for specific tasks.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures
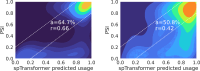
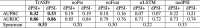
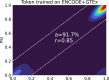
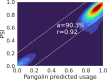
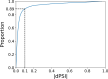
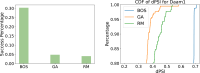
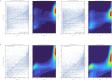
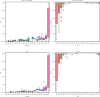
References
-
- Barash Y, Calarco JA, Gao W, Pan Q, Wang X, Shai O, Blencowe BJ, Frey BJ. Deciphering the splicing code. Nature. 2010; 465(7294):53–59. - PubMed
-
- Bend R, Cohen L, Carter MT, Lyons MJ, Niyazov D, Mikati MA, Rojas SK, Person RE, Si Y, Wentzensen IM, et al. Phenotype and mutation expansion of the PTPN23 associated disorder characterized by neurodevelopmental delay and structural brain abnormalities. European Journal of Human Genetics. 2020; 28(1):76–87. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
