This is a preprint.
Vaccination with mRNA-encoded membrane-bound HIV Envelope trimer induces neutralizing antibodies in animal models
- PMID: 39896562
- PMCID: PMC11785158
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.01.24.634423
Vaccination with mRNA-encoded membrane-bound HIV Envelope trimer induces neutralizing antibodies in animal models
Update in
-
Vaccination with an mRNA-encoded membrane-bound HIV envelope trimer induces neutralizing antibodies in animal models.Sci Transl Med. 2025 Jul 30;17(809):eadw0721. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adw0721. Epub 2025 Jul 30. Sci Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40737430 Free PMC article.
Abstract
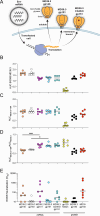
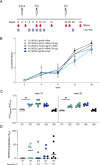
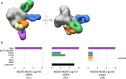
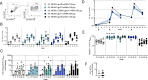
A protective vaccine against HIV will likely need to induce broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) that engage relatively conserved epitopes on the HIV envelope glycoprotein (Env) trimer. Nearly all vaccine strategies to induce bnAbs require the use of relatively complex immunization regimens involving a series of different immunogens, most of which are Env trimers. Producing protein-based clinical material to evaluate such relatively complex regimens in humans presents major challenges in cost and time. Furthermore, immunization with HIV trimers as soluble proteins induces strong non-neutralizing responses to the trimer base, which is normally occluded on the virion. These base responses could potentially detract from the induction of nAbs and the eventual induction of bnAbs. mRNA vaccine platforms offer potential advantages over protein delivery for HIV vaccine development, including increased production speed, reduced cost, and the ability to deliver membrane-bound trimers that might facilitate improved immuno-focusing to non-base epitopes. We report the design of mRNA-delivered soluble and membrane-bound forms of a stabilized native-like Env trimer (BG505 MD39.3), initial immunogenicity evaluation in rabbits that triggered clinical evaluation, and more comprehensive evaluation of B cell, T cell, and antibody responses in non-human primates. mRNA-encoded membrane-bound Env immunization elicited reduced off-target base-directed Env responses and stronger neutralizing antibody responses, compared with mRNA-encoded soluble Env. Overall, mRNA delivery of membrane-bound Env appears promising for enhancing B cell responses to subdominant epitopes and facilitating rapid translation to clinical testing, which should assist HIV vaccine development.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.M.S and W.R.S. are inventors on a patent for the BG505 MD39 immunogen (US11203617B2). S.H. and W.R.S. are employees and shareholders of Moderna, Inc. D.J.I. and S.C. are inventors on a patent for the SMNP adjuvant (US11547672B2). All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
