This is a preprint.
STAT3 phosphorylation in the rheumatoid arthritis immunological synapse
- PMID: 39896614
- PMCID: PMC11785017
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.01.20.633875
STAT3 phosphorylation in the rheumatoid arthritis immunological synapse
Update in
-
STAT3 phosphorylation in the rheumatoid arthritis immunological synapse.J Autoimmun. 2025 Jul;155:103456. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2025.103456. Epub 2025 Jul 2. J Autoimmun. 2025. PMID: 40609233
Abstract
Targeting the JAK/STAT pathway has emerged as a key therapeutic strategy for managing Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). JAK inhibitors suppress cytokine-mediated signaling, including the critical IL-6/STAT3 axis, thereby effectively targeting different aspects of the pathological process. However, despite their clinical efficacy, a subset of RA patients remains refractory to JAK inhibition, underscoring the need for alternative approaches. Here, we identify a novel JAK-independent mechanism of STAT3 activation, which is triggered by the formation of the immunological synapse (IS) in naïve CD4+ T cells. Our data demonstrates that Lck mediates the TCR-dependent phosphorylation of STAT3 at the IS, highlighting this pathway as a previously unrecognized hallmark of early T cell activation. Furthermore, we show that the synaptic Lck/TCR-STAT3 pathway is compromised in RA. This discovery highlights a new therapeutic target for RA beyond JAK inhibitors, offering potential avenues for treating patients resistant to current therapies.
Keywords: CD4 T cells; Immunological synapse; Jak inhibitors; Lck; Rheumatoid arthritis; STAT3.
Conflict of interest statement
7.CONFLICT OF INTEREST DECLARATION This work was supported in part by a Research Agreement with Cue Biopharma for basic research on cytokine signalling pathways in the immunological synapse. AJ and MLD are founders at Granza Bio.
Figures

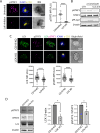
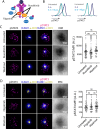
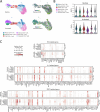
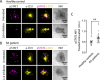
References
-
- Wegner N., et al. , Autoimmunity to specific citrullinated proteins gives the first clues to the etiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev, 2010. 233(1): p. 34–54. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
