This is a preprint.
Benchmarking and optimizing Perturb-seq in differentiating human pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 39896670
- PMCID: PMC11785042
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.01.21.633969
Benchmarking and optimizing Perturb-seq in differentiating human pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
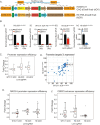
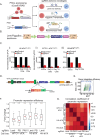
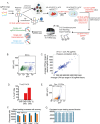
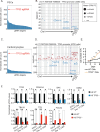
Perturb-seq is a powerful approach to systematically assess how genes and enhancers impact the molecular and cellular pathways of development and disease. However, technical challenges have limited its application in stem cell-based systems. Here, we benchmarked Perturb-seq across multiple CRISPRi modalities, on diverse genomic targets, in multiple human pluripotent stem cells, during directed differentiation to multiple lineages, and across multiple sgRNA delivery systems. To ensure cost-effective production of large-scale Perturb-seq datasets as part of the Impact of Genomic Variants on Function (IGVF) consortium, our optimized protocol dynamically assesses experiment quality across the weeks-long procedure. Our analysis of 1,996,260 sequenced cells across benchmarking datasets reveals shared regulatory networks linking disease-associated enhancers and genes with downstream targets during cardiomyocyte differentiation. This study establishes open tools and resources for interrogating genome function during stem cell differentiation.
Figures

References
-
- Jaitin D. A. et al. Dissecting immune circuits by linking CRISPR-pooled screens with single-cell RNA-seq. Cell 167, 1883–1896.e15 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
