Severe metabolic accumulation of VV116 in kidney transplant patients with impaired renal function: a case series report
- PMID: 39896812
- PMCID: PMC11782228
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1501813
Severe metabolic accumulation of VV116 in kidney transplant patients with impaired renal function: a case series report
Abstract
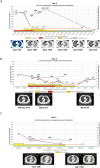
The treatment of COVID-19 in the post-transplant individuals is challenging, primarily due to the drug-drug interaction between nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and tacrolimus. Deuremidevir hydrobromide tablets (VV116) is an orally small molecule agents target SARS-CoV-2 RdRp and inhibits viral replication. It may have a low likelihood of drug-drug interactions and has a potential to provide new treatment option. We described three cases of renal transplant patients with concomitant impaired renal function who developed COVID-19 pneumonia and were treated with VV116. Despite varying degrees of drug accumulation, these patients achieved rapid viral clearance and showed prompt improvement in pneumonia symptoms. Notably, tacrolimus blood concentrations remained within the therapeutic range throughout treatment, and no clinically significant adverse events were observed despite the drug accumulation.
Keywords: COVID-19; VV116; drug accumulation; kidney dysfunction; organ transplant.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Gao, Miao, Wang, Zhou, Gao, Liu, Wu, Ma, Zhou, Yang, Meng, Feng, Zhao, Liu, Mou, Kang, Liang and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
YG declares receiving consulting fees from Sinovac and lecture fees from Pfizer over the past 36 months. Authors KM, LZ, and YY were employed by United-Power Pharma Tech Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Villar PME, Mendes PRA, Kiyota TA, Engleitner HA, Tamesawa CS, Morello MM, et al. Oximetry at Admission as a Predictor of Tomographic and Functional Impairment after 3-6 Months in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19. J Int Med Res. (2023) 51:3000605231177187. doi: 10.1177/03000605231177187 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

