Antiviral efficacy of fluoxetine in early symptomatic COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial (PLATCOV)
- PMID: 39896880
- PMCID: PMC11787712
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036
Antiviral efficacy of fluoxetine in early symptomatic COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial (PLATCOV)
Abstract
Background: The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) fluoxetine and fluvoxamine were repurposed for the treatment of early COVID-19 based on their antiviral activity in vitro, and observational and clinical trial evidence suggesting they prevented progression to severe disease. However, these SSRIs have not been recommended in therapeutic guidelines and their antiviral activity in vivo has not been characterised.
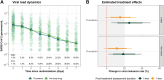
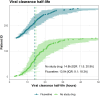
Methods: PLATCOV is an open-label, multicentre, phase 2, randomised, controlled, adaptive pharmacometric platform trial running in Thailand, Brazil, Pakistan, and Laos. We recruited low-risk adult outpatients aged 18-50 with early symptomatic COVID-19 (symptoms <4 days) between 5 April 2022 and 8 May 2023. Patients were assigned using block randomisation to one of eleven treatment arms including oral fluoxetine (40 mg/day for 7 days), or no study drug. Uniform randomisation ratios were applied across the active treatment groups while the no study drug group comprised ≥20% of patients at all times. The primary endpoint was the rate of oropharyngeal viral clearance assessed until day 7. Measurements were taken daily between days 0 and 7 and analysed in a modified intention-to-treat population (>2 days follow-up).The viral clearance rate was estimated under a Bayesian hierarchical linear model fitted to the log10 viral densities measured in standardised duplicate oropharyngeal swab eluates taken daily over one week (18 measurements per patient). Secondary endpoints were all-cause hospital admission at 28 days, and time to resolution of fever and symptoms. This ongoing trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT05041907).
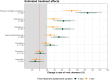
Findings: 271 patients were concurrently randomised to either fluoxetine (n = 120) or no study drug (n = 151). All patients had received at least one COVID-19 vaccine dose and 67% were female (182/271). In the primary analysis, viral clearance rates following fluoxetine were compatible with a small or no increase relative to the no study drug arm (15% increase; 95% credible interval (CrI): -2 to 34%). There were no deaths or hospitalisations in either arm. There were no significant differences in times to symptom resolution or fever clearance between the fluoxetine and the no study drug arms (although only a quarter of patients were febrile at baseline). Fluoxetine was well tolerated, there were no serious adverse events and only one grade 3 adverse event in the intervention arm.
Interpretation: Overall, the evidence from this study is compatible with fluoxetine having a weak in vivo antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2, although the primary endpoint is also compatible with no effect. This level of antiviral efficacy is substantially less than with other currently available antiviral drugs.
Funding: Wellcome Trust Grant ref: 223195/Z/21/Z through the COVID-19 Therapeutics Accelerator.
Keywords: Antivirals; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Viral clearance.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zhuang W., Xu J., Wu Y. Post-marketing safety concerns with nirmatrelvir: a disproportionality analysis of spontaneous reports submitted to the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2023;9:2830–2842. - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

