Pulmonary Coinfection of Pneumocystis jirovecii and Aspergillus Species
- PMID: 39896987
- PMCID: PMC11786051
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofaf018
Pulmonary Coinfection of Pneumocystis jirovecii and Aspergillus Species
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Pulmonary Coinfection of Pneumocystis jirovecii and Aspergillus Species.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 17;12(2):ofaf083. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaf083. eCollection 2025 Feb. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39963700 Free PMC article.
Abstract
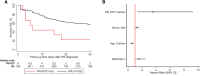
In this multicenter study of 387 patients who were immunocompromised, 4.5% with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis also had Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. Predictors of coinfection included elevated β-D-glucan and prolonged corticosteroid use. Coinfection correlated with reduced 30-day survival (22% vs 57%), suggesting that early identification and prophylaxis may improve outcomes.
Keywords: PCP-IPA coinfection; Pneumocystis jirovecii; aspergillosis; immunocompromised patients; invasive pulmonary aspergillosis.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. M. H. received research funding from Gilead, Astellas, MSD, IMMY, Pulmocide, Shionogi, Melinta, Mundipharma, Scynexis, F2G, and Pfizer, all unrelated to the submitted work. R. K. received research grants from Merck and Pfizer, both unrelated to the submitted work. All other authors report no potential conflicts.
Figures
References
-
- Markantonatou A, Ioakimidou A, Arvaniti K, et al. Pulmonary co-infections by Pneumocystis jirovecii and Aspergillus fumigatus in non-HIV patients: a report of two cases and literature review. Mycoses 2017; 60:626–33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

