A machine learning-based radiomics approach for differentiating patellofemoral osteoarthritis from non-patellofemoral osteoarthritis using Q-Dixon MRI
- PMID: 39896989
- PMCID: PMC11782249
- DOI: 10.3389/fspor.2025.1535519
A machine learning-based radiomics approach for differentiating patellofemoral osteoarthritis from non-patellofemoral osteoarthritis using Q-Dixon MRI
Abstract
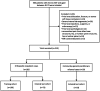
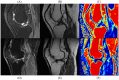
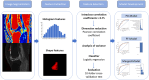
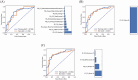
This prospective diagnostic study aimed to assess the utility of machine learning-based quadriceps fat pad (QFP) radiomics in distinguishing patellofemoral osteoarthritis (PFOA) from non-PFOA using Q-Dixon MRI in patients presenting with anterior knee pain. This diagnostic accuracy study retrospectively analyzed data from 215 patients (mean age: 54.2 ± 11.3 years; 113 women). Three predictive models were evaluated: a proton density-weighted image model, a fat fraction model, and a merged model. Feature selection was conducted using analysis of variance, and logistic regression was applied for classification. Data were collected from training, internal, and external test cohorts. Radiomics features were extracted from Q-Dixon MRI sequences to distinguish PFOA from non-PFOA. The diagnostic performance of the three models was compared using the area under the curve (AUC) values analyzed with the Delong test. In the training set (109 patients) and internal test set (73 patients), the merged model exhibited optimal performance, with AUCs of 0.836 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.762-0.910] and 0.826 (95% CI: 0.722-0.929), respectively. In the external test set (33 patients), the model achieved an AUC of 0.885 (95% CI: 0.768-1.000), with sensitivity and specificity values of 0.833 and 0.933, respectively (p < 0.001). Fat fraction features exhibited a stronger predictive value than shape-related features. Machine learning-based QFP radiomics using Q-Dixon MRI accurately distinguishes PFOA from non-PFOA, providing a non-invasive diagnostic approach for patients with anterior knee pain.
Keywords: Q-Dixon MRI; anterior knee pain; fat fraction; machine learning; patellofemoral osteoarthritis; quadriceps fat pad; radiomics.
© 2025 Lyu, Ren, Lu, Zhong, Song, Li and Yao.
Conflict of interest statement
YS, from Siemens Healthineers Ltd., was an MR collaboration scientist providing technical support for this study under Siemens collaboration regulation without any compensation or personal interest pertaining to this study. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Collins NJ, Oei EHG, de Kanter JL, Vicenzino B, Crossley KM. Prevalence of radiographic and magnetic resonance imaging features of patellofemoral osteoarthritis in young and middle-aged adults with persistent patellofemoral pain. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). (2019) 71:1068–73. 10.1002/acr.23726 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

