Global trends and emerging insights in BRAF and MEK inhibitor resistance in melanoma: a bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 39897423
- PMCID: PMC11782018
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1538743
Global trends and emerging insights in BRAF and MEK inhibitor resistance in melanoma: a bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to perform a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of global research on BRAF and MEK inhibitor resistance in melanoma, identifying key research trends, influential contributors, and emerging themes from 2003 to 2024.
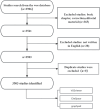
Methods: A systematic search was conducted in the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database to retrieve publications related to BRAF and MEK inhibitor resistance from 1 January 2003, to 1 September 2024. Bibliometric analyses, including publication trends, citation networks, and keyword co-occurrence patterns, were performed using VOSviewer and CiteSpace. Collaborative networks, co-cited references, and keyword burst analyses were mapped to uncover shifts in research focus and global cooperation.
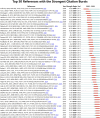
Results: A total of 3,503 documents, including 2,781 research articles and 722 review papers, were analyzed, highlighting significant growth in this field. The United States, China, and Italy led in publication volume and citation impact, with Harvard University and the University of California System among the top contributing institutions. Research output showed three phases of growth, peaking in 2020. Keyword and co-citation analyses revealed a transition from early focus on BRAF mutations and MAPK pathway activation to recent emphasis on immunotherapy, combination therapies, and non-apoptotic cell death mechanisms like ferroptosis and pyroptosis. These trends reflect the evolving priorities and innovative approaches shaping the field of resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors in melanoma.
Conclusion: Research on BRAF and MEK inhibitor resistance has evolved significantly. This analysis provides a strategic framework for future investigations, guiding the development of innovative, multi-modal approaches to improve treatment outcomes for melanoma patients.
Keywords: BRAF mutations; MEK inhibitors; immunotherapy; melanoma; therapeutic resistance.
Copyright © 2025 Bai, Wan, Zhou, Wang, Lou, Zhang and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

