Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence Post-Ablation Across Heart Failure Categories: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 39897444
- PMCID: PMC11779678
- DOI: 10.14740/cr2020
Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence Post-Ablation Across Heart Failure Categories: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have provided evidence of reduced recurrence of atrial fibrillation (AF), all-cause mortality, and heart failure (HF) hospitalizations after catheter ablation (CA) in both HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Aggregate data comparing the efficacy of AF ablation and clinical endpoints in HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF) to HFrEF and HFpEF are lacking.
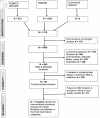
Methods: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis aimed at determining any differences in AF recurrence rate, all-cause mortality, and HF hospitalizations among patients with HFrEF, HFmrEF, and HFpEF who underwent AF ablation. A systematic search of PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases was performed until October 31, 2023.
Results: A total of seven studies comprising 3,795 patients were retained: HFrEF 1,281 (33.8%), HFmrEF 870 (22.9%), and HFpEF 1,644 (43.3%). After median follow-up of 24 months, there was no significant difference in rate of AF recurrence between the three HF categories: HFrEF 40% (30-49%), HFmrEF 35% (28-43%); and HFpEF 35% (25-45%). Only two studies which included outcomes in the three HF categories were identified. Pooled hazard ratio (HR) of all-cause mortality and HF hospitalization combined after ablation or other rhythm control compared to other conservative management were: HFrEF 0.77 (0.63 - 0.94); HFmrEF 0.81 (0.55 - 1.20); and HFpEF 0.74 (0.55 - 1.00).
Conclusions: CA has similar efficacy in the long-term resolution of AF among patients with HFrEF, HFmrEF, and HFpEF. Further studies are needed to provide a robust analysis on the potential impact of CA on all-cause mortality.
Keywords: Ablation; Atrial fibrillation; Heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction; Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
Copyright 2025, Hashem et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Atrial fibrillation and risk of adverse outcomes in heart failure with reduced, mildly reduced, and preserved ejection fraction: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2024 Apr;35(4):715-726. doi: 10.1111/jce.16209. Epub 2024 Feb 13. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2024. PMID: 38348517
-
Outcomes of Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Heart Failure Subtypes.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2024 Sep;17(9):e012926. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.124.012926. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2024. PMID: 39193716
-
Prevalence and Prognostic Implication of Atrial Fibrillation in Heart Failure Subtypes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Heart Lung Circ. 2023 Jun;32(6):666-677. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2023.02.009. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Heart Lung Circ. 2023. PMID: 37003940
-
Atrial Fibrillation in Heart Failure With Preserved, Mid-Range, and Reduced Ejection Fraction.JACC Heart Fail. 2017 Aug;5(8):565-574. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2017.05.001. Epub 2017 Jul 12. JACC Heart Fail. 2017. PMID: 28711451
-
Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Heart Failure With Reduced vs Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JAMA Cardiol. 2024 Jun 1;9(6):545-555. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2024.0675. JAMA Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38656292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mountantonakis SE, Grau-Sepulveda MV, Bhatt DL, Hernandez AF, Peterson ED, Fonarow GC. Presence of atrial fibrillation is independently associated with adverse outcomes in patients hospitalized with heart failure: an analysis of get with the guidelines-heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. 2012;5(2):191–201. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.111.965681. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kroshian G, Joseph J, Kinlay S, Peralta AO, Hoffmeister PS, Singh JP, Yuyun MF. Atrial fibrillation and risk of adverse outcomes in heart failure with reduced, mildly reduced, and preserved ejection fraction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2024;35(4):715–726. doi: 10.1111/jce.16209. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Naka KK, Bazoukis G, Bechlioulis A, Korantzopoulos P, Michalis LK, Ntzani EE. Association between atrial fibrillation and patient-important outcomes in heart failure patients with implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes. 2019;5(2):96–104. doi: 10.1093/ehjqcco/qcy054. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
