The anti-staphylococcal activity (planktonic and biofilm) of Cnestis ferruginea is due to benzoquinone, the oxidation product of hydroquinone
- PMID: 39897480
- PMCID: PMC11782209
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1494589
The anti-staphylococcal activity (planktonic and biofilm) of Cnestis ferruginea is due to benzoquinone, the oxidation product of hydroquinone
Abstract
Introduction: Cnestis ferruginea is used frequently in African traditional medicine for treating infectious diseases. Previous bioassay-guided purification has identified hydroquinone as the major bio-active compound in the aforementioned plant, responsible for its antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus. While the phenol hydroquinone can be directly extracted from the plant, it may undergo (reversible) oxidation under mild conditions to yield benzoquinone, a compound with known antimicrobial activity against i.a. S. aureus.
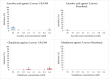
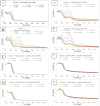
Methods: We, examined whether hydroquinone or its oxidation product, benzoquinone, is the active compound against bacteria such as S. aureus. To achieve this we performed broth microdilution (planktonic) and biofilm activity tests against two different strains of S. aureus. The inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of benzoquinone and hydroquinone under various circumstances were compared, assessing their stability, and examining their effectiveness against two strains of S. aureus (Rosenbach and USA 300) in both planktonic and biofilm environments.
Results: Benzoquinone demonstrated antibacterial activity against S. aureus Rosenbach and USA 300 with IC50 of 6.90 ± 2.30 mM and 7.72 ± 2.73 mM, respectively, while the corresponding values for hydroquinone were 15.63 ± 2.62 mM and 19.21 ± 4.84 mM, respectively. However, when oxidation was prevented by the addition of antioxidants such as ascorbic acid or glutathione, hydroquinone lost its antibacterial property, while benzoquinone retained activity. Comparing conditions in which hydroquinone could convert into benzoquinone against conditions in which this conversion was inhibited, showed that hydroquinone alone did not inhibit bacterial growth of S. aureus, while benzoquinone alone did.
Discussion: These results prove that the oxidation product benzoquinone is responsible for the antimicrobial activity previously ascribed to hydroquinone.
Keywords: Cnestis ferruginea; S. aureus; benzoquinone; biofilm; hydroquinone; oxidation.
Copyright © 2025 Panda, Reynders, Kipanga and Luyten.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- Carcamo-Noriega E. N., Sathyamoorthi S., Banerjee S., Gnanamani E., Mendoza-Trujillo M., Mata-Espinosa D., et al. . (2019). 1,4-Benzoquinone antimicrobial agents against Staphylococcus aureus and Mycobacterium tuberculosis derived from scorpion venom. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 116, 12642–12647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1812334116 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (2010). Antimicrobial resistance surveillance in Europe 2009. Annual Report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net). Stockholm: ECDC.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

