Betaine inhibits the stem cell-like properties of hepatocellular carcinoma by activating autophagy via SAM/m6A/YTHDF1-mediated enhancement on ATG3 stability
- PMID: 39897540
- PMCID: PMC11780527
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.102682
Betaine inhibits the stem cell-like properties of hepatocellular carcinoma by activating autophagy via SAM/m6A/YTHDF1-mediated enhancement on ATG3 stability
Abstract
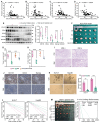
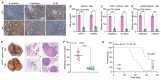
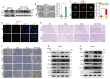
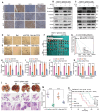
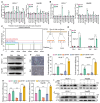
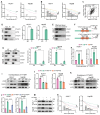
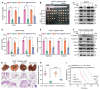
Background: Stem cell-like properties are known to promote the recurrence and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), contributing to a poor prognosis for HCC patients. Betaine, an important phytochemical and a methyl-donor related substance, has shown protective effects against liver diseases. However, its effect on HCC stem cell-like properties and the underlying mechanisms remains uninvestigated. Methods: We measured the effects of betaine on the stem cell-like properties and malignant progression of HCC using patient-derived xenografts, cell-derived xenografts, tail vein-lung metastasis models, in vitro limiting dilution, tumor sphere formation, colony formation, and transwell assays. Mechanistic exploration was conducted using western blots, dot blots, methylated RNA immunoprecipitation-qPCR, RNA stability assays, RNA immunoprecipitation-qPCR, RNA pull-down, and gene mutation assays. Results: A cohort study of HCC found that a higher serum concentration of betaine was associated with decreased levels of stemness-related markers. Furthermore, in HCC cells and xenograft mice, betaine suppressed the stem cell-like properties of HCC by activating autophagy. Mechanistically, betaine increased the m6A modification in HCC by producing S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) via betaine-homocysteine S-methyltransferase (BHMT). This increase in SAM subsequently triggered autophagy by enhancing the stability of autophagy-related protein 3 (ATG3) via YTHDF1 in an m6A-dependent manner, thereby inhibiting the stem cell-like properties of HCC cells. Conclusions: These findings indicate that betaine inhibits the stem cell-like properties of HCC via the SAM/m6A/YTHDF1/ATG3 pathway. This study underscores the potential anti-tumor effects of betaine on HCC and offers novel therapeutic prospects for HCC patients.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; autophagy; betaine; hepatocellular carcinoma; stem cell-like properties.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Vogel A, Meyer T, Sapisochin G, Salem R, Saborowski A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2022;400:1345–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

