Discovering the key symptoms for identifying patterns in functional dyspepsia patients: Doctor's decision and machine learning
- PMID: 39897574
- PMCID: PMC11786057
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imr.2024.101115
Discovering the key symptoms for identifying patterns in functional dyspepsia patients: Doctor's decision and machine learning
Abstract
Background: Pattern identification is a crucial diagnostic process in Traditional East Asian Medicine, classifying patients with similar symptom patterns. This study aims to identify key symptoms for distinguishing patterns in patients with functional dyspepsia (FD) using explicit (doctor's decision-based) and implicit (computational model-based) approaches.
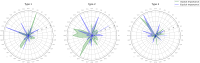
Methods: Data from twenty-one FD patients were collected from local clinics of traditional Korean Medicine and provided to three doctors in a standardized format. Each doctor identified patterns among three types: spleen-stomach weakness, spleen deficiency with qi stagnation/liver-stomach disharmony, and food retention. Doctors evaluated the importance of the symptoms indicated by items in the Standard Tool for Pattern Identification of Functional Dyspepsia questionnaire. Explicit importance was determined through doctors' survey by general evaluation and by selecting specific information used for the diagnosis of patient cases. Implicit importance was assessed by feature importance from the random forest classification models, which classify three types for general differentiation and perform binary classification for specific types.
Results: Key symptoms for distinguishing FD patterns were identified using two approaches. Explicit importance highlighted dietary and nausea-related symptoms, while implicit importance identified complexion or chest tightness as generally crucial. Specific symptoms important for particular pattern types were also identified, and significant correlation between implicit and explicit importance scores was observed for types 1 and 3.
Conclusion: This study showed important clinical information for differentiating FD patients using real patient data. Our findings suggest that these approaches can contribute to developing tools for pattern identification with enhanced accuracy and reliability.
Keywords: Functional dyspepsia; Machine learning; Pattern identification; Symptom importance; Syndrome differentiation.
© 2025 Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Ferreira A.S., Lopes A.J. Chinese medicine pattern differentiation and its implications for clinical practice. Chin J Integr Med. 2011;17(11):818–823. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J., Chen T., Wen Y., Siah K.T.H., Tang X. Insights and future prospects of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of functional dyspepsia. Phytomedicine. 2024;127 - PubMed
-
- Zhou W., Su J., Zhang H. Efficacy and safety of acupuncture for the treatment of functional dyspepsia: meta-analysis. J Altern Complement Med. 2016;22(5):380–389. - PubMed
-
- Ha N.Y., Jeong H., Lee H., Ko S.J., Park J.W., Kim J. Safety and effectiveness of traditional herbal medicine Siho-sogan-san in functional dyspepsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;313 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

