Biodesulfurization enhancement via targeted re-insertion of the flavin reductase dszD in the genome of the model strain Rhodococcus qingshengii IGTS8
- PMID: 39897813
- PMCID: PMC11783014
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41899
Biodesulfurization enhancement via targeted re-insertion of the flavin reductase dszD in the genome of the model strain Rhodococcus qingshengii IGTS8
Abstract
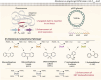
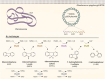
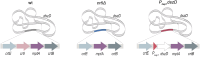
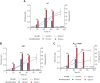
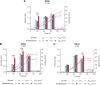
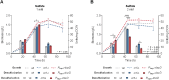
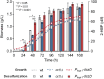
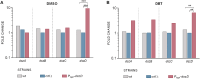
Biodesulfurization (BDS) has emerged as an alternative to the excessively costly hydrodesulfurization of recalcitrant heterocyclic sulfur compounds, such as dibenzothiophene (DBT) and its derivatives. The model desulfurizing strain Rhodococcus qingshengii IGTS8 is responsible for the removal of sulfur through the 4S metabolic pathway, operating through a plasmid-borne dszABC operon, as well as the chromosomal gene for the flavin reductase, d szD. However, naturally occurring biocatalysts do not exhibit the required BDS activity to be useful for industrial applications and for this reason, genetic modifications are currently being explored. Here, we constructed a genetically modified R. qingshengii IGTS8 strain, which carries an additional copy of the flavin reductase gene dszD under the control of the rhodococcal promoter P kap1 , inserted in the neutral chromosomal genetic locus crtI. We conducted a comparative study of the growth and biodesulfurization capabilities of P kap1 -dszD, wild-type and crtIΔ strains, grown on different types and concentrations of carbon and sulfur sources. A significant enhancement of biodesulfurization activity, maximum calculated biomass, and dszD transcript levels in the presence of DBT as the sole sulfur source was achieved for the P kap1 -dszD strain paving the way for further studies that could lead to a more viable commercial biodesulfurization process.
Keywords: Actinomycetes; Biodesulfurization; Dibenzothiophene; FMN reductase; Genetic engineering; Model biocatalyst; Whole-cell biocatalyst.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Thompson D., Cognat V., Goodfellow M., Koechler S., Heintz D., Carapito C., Van Dorsselaer A., Mahmoud H., Sangal V., Ismail W. Phylogenomic classification and biosynthetic potential of the fossil fuel-biodesulfurizing Rhodococcus strain IGTS8. Front. Microbiol. 2020;11:1–11. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01417. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

