Impacts of tropical climate on outdoor treatment of anaerobically digested sanitary wastewater using native microalgae
- PMID: 39897888
- PMCID: PMC11787462
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41848
Impacts of tropical climate on outdoor treatment of anaerobically digested sanitary wastewater using native microalgae
Abstract
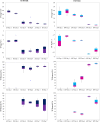
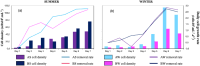
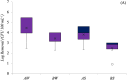
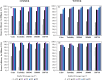
Microalgal technologies interact with other processes, enabling treatment systems to remove nutrients and pollutants while facilitating the reuse of final effluents. However, the development of these systems in various climates and their specific characteristics has been poorly studied. The objective of this work was to evaluate the influence of different tropical seasons within the Cerrado Biome on effluent treatment in a closed photobioreactor using a consortium of native microalgae. Cultivation was performed on a bench scale using anaerobically digested sanitary wastewater processed by two mechanisms from the wastewater treatment plant in Bauru, Brazil: the Upflow Anaerobic Filter (UAF) and the Anaerobic Baffled Reactor (ABR). The cultivation took place in an outdoor area with constant aeration and under natural climatic conditions during two seasons: summer and winter. Each season's cultivation occurred in triplicate over 7 days. After cultivation, the effluent and microalgal biomass were separated using a tannin-based organic coagulant (Tanfloc SG) to evaluate effluent quality for non-potable reuse. During summer, the treatment of anaerobically digested sanitary wastewater from UAF achieved 76 ± 3 % and 84 ± 1.2 % phosphorus and nitrogen removal, respectively, while the treatment of anaerobically digested sanitary wastewater from ABR achieved 83 ± 4 % and 85 ± 3 % phosphorus and nitrogen removal, respectively. In winter, 86 ± 2 % and 89 ± 5 % of phosphorus and nitrogen, respectively, were removed from the anaerobically digested sanitary wastewater from UAF, while 68 ± 6 % and 93 ± 3 % were removed from the anaerobically digested sanitary wastewater from ABR. The removal of generic bacteria exceeded 3.0 log for most conditions, with the summer experiments showing absolute values of E. coli below 100 CFU·100 ml⁻1, indicating that the effluent could be used for unrestricted irrigation. Microalgal technology can serve as a tertiary treatment in countries with tropical climates, promoting the reintegration of water into the production cycle, which aligns with circular economy principles.
Keywords: Effluent reuse; Microalgae; Nutrient removal; Tropical climate; Wastewater treatment.
© 2025 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- UN . UN - United Nations; 2021. Progress on Wastewater Treatment – 2021 Update.https://www.unwater.org/publications/progress-on-wastewater-treatment-63...
-
- ANA, Atlas esgotos . Brasília; 2020. atualização da base de dados de estações de tratamento de esgotos no Brasil, Agência Nacional de Águas.http://atlasesgotos.ana.gov.br/
-
- Metcalf L., Eddy H.P. In: Wastewater Engineering : Treatment, Disposal, and Reuse. fourth ed. Tchobanoglous George, Burton Franklin L., David Stensel H., editors. McGraw-Hill; New York, NJ: 2003. https://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/titel/1979505
-
- Miki R.E., Miki M.K. Encontro Técnico AESABESP. 2019. Estação de TRATAMENTO de esgoto como instalação de recuperação de recursos; p. 13.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

