Exosomal miRNAs involvement in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 39897907
- PMCID: PMC11786886
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41983
Exosomal miRNAs involvement in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
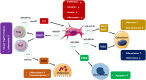
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the most common chronic autoimmune arthropathy worldwide. The initiation, and progression of RA involves multiple cellular and molecular pathways, and biological interactions. Micro RNAs (miRNAs) are characterized as a class of small non-coding RNAs that influence gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. Exosomes are biological nano-vesicles that are secreted by different types of cells. They facilitate communication and signalling between cells by transferring a variety of biological substances, such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids like mRNA and miRNA. Exosomal miRNAs were shown to be involved in normal and pathological conditions. In RA, deregulated exosomal miRNA expression was observed to be involved in the intercellular communication between synovial cells, and inflammatory or regulatory immune cells. Furthermore, circulating exosomal miRNAs were introduced as available diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for RA pathology. The current review categorized and summarized dysregulated pathologically involved and circulating exosomal miRNAs in the context of RA. It highlighted present situation and future perspective of using exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers and a specific gene therapy approach for RA treatment.
Keywords: Exosomal miRNA; Exosome; Rheumatoid arthritis; miRNA.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deregulation of exosomal miRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis patients.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 27;18(7):e0289301. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289301. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37498970 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of serum exosomal miRNA biomarkers for diagnosis of Rheumatoid arthritis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Mar 10;129:111604. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111604. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38320350
-
The pathogenic, therapeutic and diagnostic role of exosomal microRNA in the autoimmune diseases.J Neuroimmunol. 2021 Sep 15;358:577640. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2021.577640. Epub 2021 Jun 24. J Neuroimmunol. 2021. PMID: 34224949 Review.
-
Exosomal hsa-miR-335-5p and hsa-miR-483-5p are novel biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis: A development and validation study.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Jul;120:110286. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110286. Epub 2023 May 20. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37216801
-
Exosomal miRNAs in autoimmune skin diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 1;14:1307455. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1307455. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38106405 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From Gut to Lung: The Role of Bile Acids in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (RA-ILD).J Inflamm Res. 2025 Aug 2;18:10331-10340. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S524111. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40778337 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mohebbi M., Atabaki M., Tavakkol-Afshari J., Shariati-Sarabi Z., Poursamimi J., Mohajeri S.A., et al. Significant effect of Crocin on the gene expression of MicroRNA-21 and MicroRNA-155 in patients with osteoarthritis. Iran. J. Allergy, Asthma Immunol. 2022 - PubMed
-
- Niimoto T., Nakasa T., Ishikawa M., Okuhara A., Izumi B., Deie M., et al. MicroRNA-146a expresses in interleukin-17 producing T cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients. BMC Muscoskel. Disord. 2010 Sep 15;11:209. PubMed PMID: 20840794. Pubmed Central PMCID: PMC2950393. Epub 2010/09/16. eng. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Y., Sun Y., Luo Z., Lin J., Qi B., Kang X., et al. Potential mechanism underlying exercise upregulated circulating blood exosome miR-215-5p to prevent necroptosis of neuronal cells and a model for early diagnosis of alzheimer's disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022;14 PubMed PMID: 35615585. Pubmed Central PMCID: PMC9126031. Epub 2022/05/27. eng. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tomiyama E., Matsuzaki K., Fujita K., Shiromizu T., Narumi R., Jingushi K., et al. Proteomic analysis of urinary and tissue-exudative extracellular vesicles to discover novel bladder cancer biomarkers. Cancer Sci. 2021 May;112(5):2033–2045. PubMed PMID: 33721374. Pubmed Central PMCID: PMC8088963. Epub 2021/03/16. eng. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources