Transmural collaborative care model for cardiovascular risk management and medication review in patients using antipsychotics in primary care (TACTIC): A study protocol of an incomplete stepped wedge cluster randomized trial
- PMID: 39897941
- PMCID: PMC11787019
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conctc.2024.101418
Transmural collaborative care model for cardiovascular risk management and medication review in patients using antipsychotics in primary care (TACTIC): A study protocol of an incomplete stepped wedge cluster randomized trial
Abstract
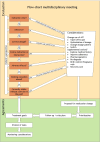
Background: It is well established that patients with severe mental illness and those treated with atypical antipsychotics (AAPs) are at an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. However, primary care currently lacks adequate monitoring of AAP usage, its effects, and the associated cardiovascular risk. We have developed TACTIC, a transmural collaborative care model for patients using AAPs prescribed by the general practitioner (GP) to address the issues of potential overtreatment with AAPs and undertreatment for cardiovascular risk. TACTIC comprises three steps: an informative video for patients, a multidisciplinary meeting, and a shared decision-making consultation with the GP.
Objectives: To evaluate TACTIC's effectiveness on cardiovascular risk and mental health and its cost-effectiveness.
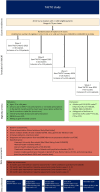
Methods: We will conduct an incomplete stepped wedge cluster randomized trial in the Netherlands.40 GP-nurse clusters are randomized into four waves. Each cluster recruits adult patients (25-85 years), without prior diagnoses of dementia, delirium, or cardiovascular disease, for whom the GP prescribes AAPs. Every five months, a new wave starts with TACTIC. Measurements are taken before the intervention starts and every 5 months until the study concludes. Primary outcomes are cardiovascular risk and mental health as measured with the QRISK3 score and MHI5, respectively. The economic evaluation consists of two cost-utility analyses, one on the data collected alongside the trial and one based on a model extrapolating the trial data to a 10-year horizon. We will also evaluate the process of delivering TACTIC.
Conclusion: This study will assess TACTIC's (cost)effectiveness and provide insights for successful delivery in general practice.
Clinical trials registration: clinicaltrials.gov NCT05647980.
Keywords: Antipsychotics; Cardiovascular risk; Collaborative care; Deprescribing; Off label; Primary health care.
© 2025 Radboud University Medical Center.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Halfdanarson O., Zoega H., Aagaard L., Bernardo M., Brandt L., Fuste A.C., et al. International trends in antipsychotic use: a study in 16 countries, 2005-2014. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017;27(10):1064–1076. - PubMed
-
- The Dutch Care Institute GIPdatabank. 2023 https://www.gipdatabank.nl/databank?infotype=g&label=00-totaal&tabel_g_0... [updated 23-08-2023. Available from:
-
- Maher A.R., Maglione M., Bagley S., Suttorp M., Hu J.H., Ewing B., et al. Efficacy and comparative effectiveness of atypical antipsychotic medications for off-label uses in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2011;306(12):1359–1369. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

