Inclusive excellence through digital learning: an undergraduate research experience to pilot cross-institutional collaboration between a historically black university and a predominantly white institution
- PMID: 39898000
- PMCID: PMC11787822
- DOI: 10.1080/14675986.2023.2180621
Inclusive excellence through digital learning: an undergraduate research experience to pilot cross-institutional collaboration between a historically black university and a predominantly white institution
Abstract
Increasing diversity in higher education and the workforce requires undergraduate students to learn to work together effectively to address scientific and social issues. Our goal is to learn how best to facilitate teamwork among students from Historically Black Universities (HBU) and Predominantly White Institutions (PWI) to promote collaborative learning. We analysed the evolving knowledge, perceptions, and attitudes of participating students as they developed close working relationships through a 'study-within-a-study' design where student pairs (one from an HBU and one from a PWI) conducted their own research project while we analysed how these students interacted with their partners. The Association of American Colleges and Universities (AACU) rubric of Intercultural Knowledge and Competence was used to develop a set of codes for assessing transcripts of student meetings. AACU defines six attributes of this rubric including cultural self-awareness, cultural worldview frameworks, empathy, verbal and nonverbal communication, curiosity, and openness. Our pilot results suggest that students willing to engage collaboratively with others from different cultural or educational backgrounds can display attributes of intercultural competence, while those not willing to engage in the collaborative process may not exhibit such competence. We also learnedthat students require the same initial preparation necessary for the assigned project.
Keywords: Collaborative learning; inclusive excellence; intercultural competence; undergraduate research experience.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
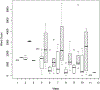
References
-
- Arasaratnam LA 2016. “Intercultural Competence.” Oxford Research Encyclopedias on Communication. doi:10.1093/acrefore/9780190228613.013.68. - DOI
-
- Association of American Colleges and Universities. “Intercultural Knowledge and Competence Rubric.” 2009. https://www.aacu.org/value/rubrics/intercultural-knowledge. Accessed August 31, 2019.
-
- Bennett MJ 1993. “Towards Ethnorelativism: A Developmental Model of Intercultural Sensitity.” In Education for the Intercultural Experience, edited by Paige RM, 22–71. Yarmouth, ME: Intercultural Press.
-
- Bennett JM 2008. “Transformative Training: Designing Programs for Culture Learning.” In Contemporary Leadership and Intercultural Competence: Understanding and Utilizing Cultural Diversity to Build Successful Organizations, edited by Moodian MA, 95–110. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
-
- Cabrera AF, Crissman JL, Bernal EM, Nora A, Terenzini PT, and Pascarella ET. 2002. “Collaborative Learning: Its Impact on College students’ Development and Diversity.” Journal of College Student Development 43 (1): 20–34.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
