Effects of oral Lcarnitine supplementation on liver enzymes in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients in the maintenance phase of treatment: a randomized clinical trial study
- PMID: 39898322
- PMCID: PMC11782257
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1507996
Effects of oral Lcarnitine supplementation on liver enzymes in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients in the maintenance phase of treatment: a randomized clinical trial study
Abstract
Background: Given that liver diseases and subsequent increases in liver enzymes are among the most frequent complications observed in leukemia patients treated with chemotherapeutic drugs, this study aimed to assess the impact of oral Lcarnitine supplementation on liver enzyme levels the maintenance phase of treatment for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) patients.
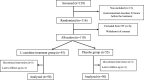
Methods: In this clinical trial, 100 pediatric patients aged >5 years were divided into two groups after obtaining informed consent. The participants were randomly divided into the Lcarnitine and placebo groups. In the Lcarnitine group, patients received 50 mg/kg of Lcarnitine syrup three times a day (every 8 h). Patients were examined for 2 months to receive Lcarnitine syrup and to measure the levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate transferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), direct bilirubin, total bilirubin, prothrombin time (PT), and partial thromboplastin time (PTT).
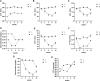
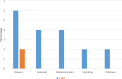
Results: The mean changes in AST, ALT, total bilirubin, and GGT during the study period were significant in the group treated with Lcarnitine (P < 0.05), although they were not significant in the placebo group (P > 0.05). Also, the levels of ALP, direct bilirubin, PT, and PTT were not significantly different between the two groups. The incidence of side effects was significantly higher in the Lcarnitine group than in the placebo group (18% vs 4%, P = 0.025).
Conclusion: The results of this study suggested that a 60-day Lcarnitine treatment can improve liver enzyme levels and thus prevent the extent of liver damage during the treatment of ALL. Based on the results of our study, Lcarnitine supplementation may have a beneficial effect on liver enzyme levels in pediatric ALL patients during the maintenance phase of treatment.
Clinical trial registration: https://irct.behdasht.gov.ir/search/result?query=IRCT20201107049296N2, identifier IRCT20201107049296N2.
Keywords: Lcarnitine; acute lymphoblastic leukemia; chemotherapy; liver enzymes; pediatric.
Copyright © 2025 Eghbali, Eghbali, Ashayeri, Fadayi, Ghaffari and Ghasemi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of oral silymarin on liver function in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the maintenance phase: a double-blind randomized clinical trial.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 12;15:1295816. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1295816. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38283627 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of fermented turmeric powder in subjects with elevated alanine transaminase levels: a randomised controlled study.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013 Mar 8;13:58. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-58. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013. PMID: 23497020 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy assessment of allogeneic human dental pulp stem cells to treat patients with severe COVID-19: structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial (Phase I / II).Trials. 2020 Jun 12;21(1):520. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04380-5. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32532356 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin supplementation effect on liver enzymes in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Nutr Rev. 2025 Jan 1;83(1):1-12. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuad166. Nutr Rev. 2025. PMID: 38213188
-
Benefits and harms of ginseng supplementation on liver function? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020 May;39:101173. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101173. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 32379697
Cited by
-
The effect of oral curcumin on vincristine-induced neuropathy in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial.BMC Cancer. 2025 Feb 25;25(1):344. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13751-7. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40000988 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Alhusaini A. M., Faddah L. M., Hasan I. H., Jarallah S. J., Alghamdi S. H., Alhadab N. M., et al. (2019). Vitamin C and turmeric attenuate Bax and Bcl-2 proteins’ expressions and DNA damage in lead acetate-induced liver injury. Dose-Response 17 (4), 1559325819885782. 10.1177/1559325819885782 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

