Estimating the minimum important difference in the ALSFRS-R-instrument in people living with MND
- PMID: 39898446
- PMCID: PMC12011019
- DOI: 10.1080/21678421.2024.2447916
Estimating the minimum important difference in the ALSFRS-R-instrument in people living with MND
Abstract
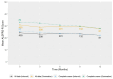
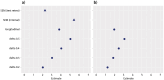
Objective: The Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale (ALSFRS-R) is a commonly used outcome measure in clinical trials for motor neuron disease (MND) therapies. As such, understanding how differences in scores relate to patient perception of their disease status is important when interpreting ALSFRS-R data. Our study sought to estimate the minimal important difference (MID) for the ALSFRS-R, the smallest difference in scores at which patients perceive a change in their quality of life. Methods: Data were collected as part of a longitudinal, observational saliva management study, ProSec3. These included both the ALSFRS-R and a global rating of change question (GRoC), which asked participants to rate how their disease had progressed since the previous visit. Anchor-based and distribution-based methods have been used to estimate the MID of the ALSFRS-R. The MID was estimated using two methods of calculating the total ALSFRS-R score, the original summation scale method and the recently proposed interval scale method. Results: A total of 145 people with MND had longitudinal ALSFRS-R and GRoC data. Different methods estimated the ALSFRS-R MID to be in the range of 2.02-5.43 for the summation scale and 1.23-3.31 for the interval scale method over a 3-month period, the time between study visits. Using anchor-based methods our MID estimates for the ALSFRS-R are 3.8 points and 2 points, respectively. Conclusions: The results of this study can guide clinicians and researchers in the interpretation of ALSFRS-R data. However, further studies are required to more precisely estimate the ALSFRS-R MID.
Keywords: ALS; ALSFRS-R; MID; MND; Motor neuron disease; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; functional rating scale; minimal important difference.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Cedarbaum JM, Stambler N, Malta E, Fuller C, Hilt D, Thurmond B, et al. . The ALSFRS-R: A revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. J Neurol Sci. 1999;169:13–21. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann P, Levy G, Montes J, Buchsbaum R, Barsdorf AI, Battista V, et al. . Excellent inter-rater, intra-rater, and telephone-administered reliability of the ALSFRS-R in a multicenter clinical trial. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2007;8:42–6. - PubMed
-
- Newton J, Jayaprakash K, Glasmacher SA, McEleney A, Bethell A, Fraser E, et al. . Excellent reliability of the ALSFRS-R administered via videoconferencing: a study of people with motor neuron disease in Scotland. J Neurol Sci. 2020. https://www.jns-journal.com/article/S0022-510X(20)30328-2/fulltext - PubMed
-
- Bakker LA, Schröder CD, Tan HHG, Vugts SMAG, Van Eijk RPA, Van Es MA, et al. . Development and assessment of the inter-rater and intra-rater reproducibility of a self-administration version of the ALSFRS-R. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020;91:75–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
