Patient-reported outcomes after immediate and delayed DIEP-flap breast reconstruction in the setting of post-mastectomy radiation therapy-results of the multicenter UMBRELLA breast cancer cohort
- PMID: 39899162
- PMCID: PMC11953195
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-025-07613-w
Patient-reported outcomes after immediate and delayed DIEP-flap breast reconstruction in the setting of post-mastectomy radiation therapy-results of the multicenter UMBRELLA breast cancer cohort
Abstract
Purpose: Timing of Deep Inferior Epigastric artery Perforator (DIEP)-flap breast reconstruction in the context of post-mastectomy radiotherapy for breast cancer patients is topic of debate. We compared the impact of immediate (before radiotherapy) versus delayed (after radiotherapy) DIEP-flap breast reconstruction (IBR versus DBR) on short- and long-term patient-reported outcomes (PROs).
Methods: Within the prospective, multicenter breast cancer cohort (UMBRELLA), we identified 88 women who underwent immediate or delayed DIEP-flap breast reconstruction and received PMRT. At 6 and 12 months post-mastectomy, as well as on long-term (≥ 12 months post-reconstruction) body image, breast symptoms, physical functioning, and pain were measured by EORTC-QLQ-30/BR23. Additionally, long-term evaluation included satisfaction with breast(s), physical well-being and self-reported adverse effects of radiation as measured by BREAST-Q, and late treatment toxicity. PROs were compared between groups using independent sample T-test.
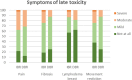
Results: IBR was performed in 56 patients (64%) and DBR in 32 patients (36%), with 15 months of median time to reconstruction. At 6 and 12 months post-mastectomy, better body image and physical functioning were observed after IBR. No statistically nor clinically relevant differences were observed in long-term EORTC and BREAST-Q outcomes (median follow-up 37-41 months for IBR vs. 42-46 months for DBR). Patients with IBR reported more fibrosis and movement restriction (median follow-up 29 vs. 61 months, resp.).
Conclusion: Long-term PROs were comparable for patients with IBR and DBR, despite more patient-reported fibrosis and movement restriction after IBR. Therefore, both treatment pathways can be considered when opting for autologous breast reconstruction in the setting of PMRT.
Keywords: Breast cancer; DIEP-flap breast reconstruction; Late radiation toxicity; Oncoplastic breast surgery; Patient-reported outcome.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Medical Research Ethics Committee (MREC) Utrecht (NL52651.041.15, MEC15/165). Consent to participate: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Figures
Comment in
-
Key considerations for interpreting patient-reported outcomes in deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap reconstruction with post-mastectomy radiotherapy.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 30;14(6):3292-3294. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2025-423. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40687226 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Protocol for a multicentre, prospective, open-label, randomised controlled trial to compare PROs and safety outcomes between preoperative and postmastectomy radiotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer patients with immediate reconstruction via a deep inferior epigastric perforator flap (CAPPELLA) in China.BMJ Open. 2025 Jan 20;15(1):e086980. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-086980. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39832996 Free PMC article.
-
The increased risk of adverse outcomes in bilateral deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap breast reconstruction compared to unilateral reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014 Feb;67(2):143-56. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2013.10.024. Epub 2013 Oct 26. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014. PMID: 24200701
-
Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap with Implant Placement has a Favorable Complication Profile Compared with Implant-Only or Flap-Only Reconstruction.J Reconstr Microsurg. 2025 Sep;41(7):631-640. doi: 10.1055/a-2483-5472. Epub 2024 Nov 25. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2025. PMID: 39587044
-
Mastectomy Alone or with Immediate Breast Reconstruction: Trend, Precipitating Factors, Patients Reported Outcome, and Oncologic Safety Analysis with and without Propensity Score Matching from 3759 Mastectomy Patients.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 Jul;49(13):3715-3727. doi: 10.1007/s00266-025-04762-7. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 40050543 Free PMC article.
-
The risk of bias of non-randomized observational studies in deep inferior epigastric perforator flap breast reconstruction: A systematic review using ROBINS-I.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2022 Nov;75(11):4096-4105. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2022.06.093. Epub 2022 Jun 29. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2022. PMID: 36117133
Cited by
-
Improving the Patient Experience in Breast Reconstruction: ERAS and Beyond.J Clin Med. 2025 Aug 7;14(15):5595. doi: 10.3390/jcm14155595. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40807212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key considerations for interpreting patient-reported outcomes in deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap reconstruction with post-mastectomy radiotherapy.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 30;14(6):3292-3294. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2025-423. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40687226 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zehra S, Doyle F, Barry M, Walsh S, Kell MR (2020) Health-related quality of life following breast reconstruction compared to total mastectomy and breast-conserving surgery among breast cancer survivors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer 27(4):534–566. 10.1007/s12282-020-01076-1 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

