Therapeutic strategies to ameliorate mitochondrial oxidative stress in ischaemia-reperfusion injury: A narrative review
- PMID: 39899361
- PMCID: PMC12204024
- DOI: 10.1042/CS20242074
Therapeutic strategies to ameliorate mitochondrial oxidative stress in ischaemia-reperfusion injury: A narrative review
Abstract
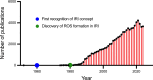
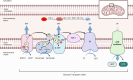
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mROS) play a crucial physiological role in intracellular signalling. However, high levels of ROS can overwhelm antioxidant defences and lead to detrimental modifications in protein, lipid and DNA structure and function. Ischaemia-reperfusion injury is a multifaceted pathological state characterised by excessive production of mROS. There is a significant clinical need for therapies mitigating mitochondrial oxidative stress. To date, a variety of strategies have been investigated, ranging from enhancing antioxidant reserve capacity to metabolism reduction. While success has been achieved in non-clinical models, no intervention has yet successfully transitioned into routine clinical practice. In this article, we explore the different strategies investigated and discuss the possible reasons for the lack of translation.
Keywords: antioxidant; ischaemia-reperfusion injury; mROS; mitochondria; oxidative stress.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.D. and M.S. are developing thiometallates for the treatment of ischaemia-reperfusion injury.
Figures


References
-
- Jennings R.B., Sommers H.M., Smyth G.A., Flack H.A., Linn H. Myocardial necrosis induced by temporary occlusion of a coronary artery in the dog. Arch. Pathol. 1960;70:68–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

