The effect of prenatal balanced energy and protein supplementation on gestational weight gain: An individual participant data meta-analysis in low- and middle-income countries
- PMID: 39899474
- PMCID: PMC11790098
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004523
The effect of prenatal balanced energy and protein supplementation on gestational weight gain: An individual participant data meta-analysis in low- and middle-income countries
Abstract
Background: Understanding the effects of balanced energy and protein (BEP) supplements on gestational weight gain (GWG) and how the effects differ depending on maternal characteristics and the nutritional composition of the supplements will inform the implementation of prenatal BEP interventions.
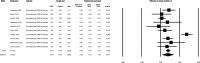
Methods and findings: Individual participant data from 11 randomized controlled trials of prenatal BEP supplements (N = 12,549, with 5,693 in the BEP arm and 6,856 in the comparison arm) in low- and middle-income countries were used. The primary outcomes included GWG adequacy (%) and the estimated total GWG at delivery as continuous outcomes, and severely inadequate (<70% adequacy), inadequate GWG (<90% adequacy), and excessive GWG (>125% adequacy) as binary outcomes; all variables were calculated based on the Institute of Medicine recommendations. Linear and log-binomial models were used to estimate study-specific mean differences or risk ratios (RRs), respectively, with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of the effects of prenatal BEP on the GWG outcomes. The study-specific estimates were pooled using meta-analyses. Subgroup analyses were conducted by individual characteristics. Subgroup analyses and meta-regression were conducted for study-level characteristics. Compared to the comparison group, prenatal BEP led to a 6% greater GWG percent adequacy (95% CI: 2.18, 9.56; p = 0.002), a 0.59 kg greater estimated total GWG at delivery (95% CI, 0.12, 1.05; p = 0.014), a 10% lower risk of severely inadequate GWG (RR: 0.90; 95% CI: 0.83, 0.99; p = 0.025), and a 7% lower risk of inadequate GWG (RR: 0.93; 95% CI: 0.89, 0.97; p = 0.001). The effects of prenatal BEP on GWG outcomes were stronger in studies with a targeted approach, where BEP supplements were provided to participants in the intervention arm under specific criteria such as low body mass index or low GWG, compared to studies with an untargeted approach, where BEP supplements were provided to all participants allocated to the intervention arm.
Conclusions: Prenatal BEP supplements are effective in increasing GWG and reducing the risk of inadequate weight gain during pregnancy. BEP supplementation targeted toward pregnant women with undernutrition may be a promising approach to delivering the supplements.
Copyright: © 2025 Wang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Rasmussen KM, Yaktine AL. Committee to reexamine IOM pregnancy weight guidelines. Food and Nutrition Board, Board on Children, Youth and Families, Institute of Medicine, National Research Council Weight gain during pregnancy: reexamining the guidelines Washington, DC: National Academies Press. 2009. - PubMed
-
- Siega-Riz AM, Viswanathan M, Moos M-K, Deierlein A, Mumford S, Knaack J, et al. A systematic review of outcomes of maternal weight gain according to the Institute of Medicine recommendations: birthweight, fetal growth, and postpartum weight retention. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;201(4):339:e1–. e14. - PubMed
-
- Perumal N, Wang D, Darling AM, Liu E, Wang M, Ahmed T, et al. Suboptimal gestational weight gain and neonatal outcomes in low and middle income countries: individual participant data meta-analysis. BMJ. 2023;382:e072249. Epub 20230921. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2022-072249 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC10512803. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

